Hot and Cold Wallet Architecture

Hot and cold wallets are both necessities for safely storing your crypto assets. When the former is used to send and receive crypto tokens, the latter securely holds your accumulating cryptocurrencies without vulnerabilities. As hot wallets require an internet connection to send and receive tokens, they are largely at risk of crypto attacks that prove to be hugely expensive. So, it cannot hold a large sum of tokens. Here is where the usage of cold wallets comes into play. Utilizing both hot and cold wallets is a safe practice in crypto vulnerability management, leaving no loopholes for attackers.
Let us understand the hot and cold wallet architecture and how it should be set up to mitigate the risk of vulnerabilities.
- What are hot wallets?
- What are cold wallets?
- Hot wallet vs Cold Wallet: Differences
- Hot and cold wallet setup
- How does hot and cold wallet interact?
- How do hot and cold wallet setups in big systems work?
What are hot wallets?
Hot wallets are crypto wallets that are always connected to the internet and are more easily accessible for users than cold wallets. They can be mobile, desktop or web-based wallets, and are user-friendly and facilitate easy transfer of currencies between crypto users.
Private keys are kept and encrypted on the app itself in hot wallets and stored online. It has hidden vulnerabilities, and hackers can target it to break into the system. Due to its ease of use, it is the most preferred wallet for buying and trading cryptocurrencies or cashing out assets after a while.
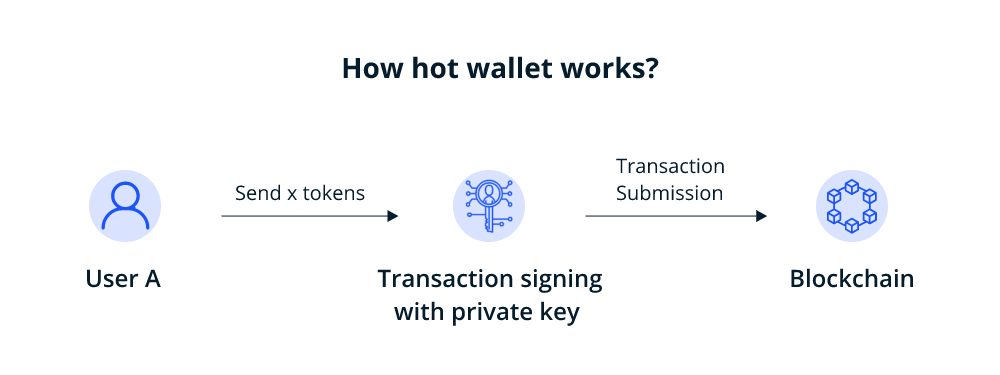
How does a hot wallet storage work?
When you install a hot wallet storage into your computer or device, it allows you to buy, send and receive crypto assets without really holding any crypto. Rather it holds the private keys using which a user can initiate transactions. This is possible, as it interacts with the blockchain storing your assets.
Metamask is one of the most popular hot wallets available today. So, we will explain how a hot wallet works using Metamask.
Metamask is available as a web browser extension that acts as a bridge between the blockchain, especially Ethereum, and your browser. When you download and install Metamask and add it as your browser extension, you will be asked to either ‘import wallet’ or ‘create a wallet.’ Import wallet allows you to add an existing wallet by typing a secret recovery phrase, while the latter enables creating a new crypto wallet.
If you create a new wallet, you need to set a new Metamask password to secure the app or platform on your device. This password can be a string of characters, face recognition, or even a fingerprint that you can regularly use to access the app, instead of a secret recovery phrase.
Once you create a password, you must copy the secret backup phrase and paste it or write it down in a safe place. For each account you have in your Metamask wallet, you will be provided with a private key. You can unlock your cryptocurrencies using this private key.
What are cold wallets?
Cold wallets are hardware-based and exist offline. Although a cold wallet is not as convenient to use as a hot wallet, it is far more secure. Using this offline wallet keeps your keys entirely protected from online hackers. Cold wallets can be paper wallets or hardware devices.
A paper wallet is a traditional way of keeping private and public keys written down or printed on paper. It is a safe way to store keys as it is not prone to phishing attacks. Hardware wallets are external devices in the form of a USB or Bluetooth device that stores your keys. As they offer less liquidity, cold wallets are best for people planning to buy and hold their crypto assets for a long period.
To do transactions between an offline cold wallet and an online hot wallet, you need to connect the hardware device to another device with internet accessibility, mostly a computer, using a plug, then transfer the required amount from the cold wallet to the hot wallet.
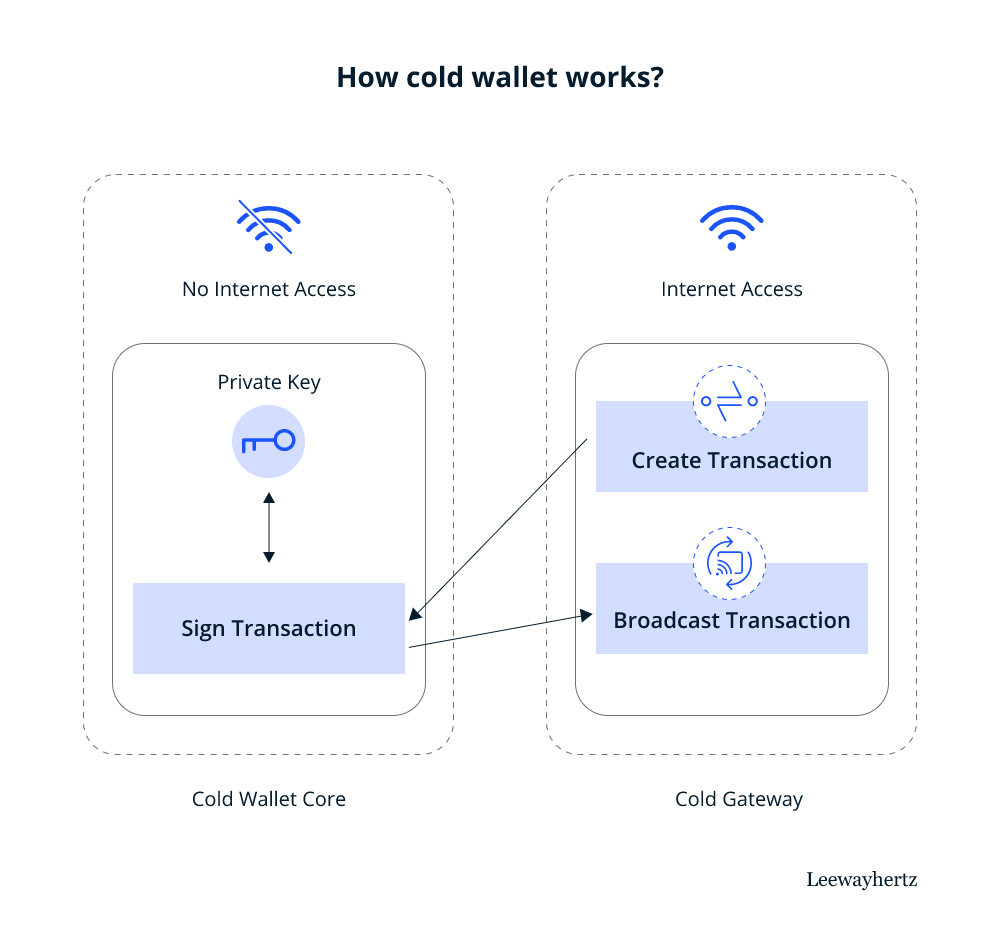
How does a cold wallet storage work?
A cold wallet, on its own, cannot connect to a blockchain and complete a transaction. When a user wants to use a cold wallet for transactions, it needs to be connected to a device with an internet connection. However, this does not put your private key under security threat. Let us see how it works.
A cold wallet storage can be roughly divided into two components, a cold wallet core and a cold gateway. While a cold wallet core has no internet access and is completely air-gapped, a cold gateway is connected to the internet. A transaction is created in the cold gateway in a cold wallet, which is then signed in the offline cold wallet core. So, if a user wants to send x number of tokens to another wallet, the transaction will be created in the cold gateway with an internet connection, but the transaction signing will be done offline. After the transaction is signed, it is disclosed or broadcast online in the cold wallet core.
Let us take the example of the cold wallet ELLIPAL to understand this better. ELLIPAL is an air-gapped hardware wallet that is essentially a secure cold wallet. It is entirely isolated from the internet and is designed to prevent unauthorized access, hacks, malware and other online attacks. So, to initiate transactions, the users need to install the ELLIPAL mobile app, acting as a proxy for it to connect to the blockchain. The whole process of transactions via an ELLIPAL wallet can be summarized into the following steps:
- The user initiates a transaction on the app.
- The app asks for confirmation from the cold wallet.
- The hardware wallet signs the transaction via a private key.
- After approval, the app completes the transaction
Hot wallet vs Cold Wallet: Differences
|
|
Hot Wallet
|
Cold Wallet
|
|---|---|---|
| Internet Connectivity | Online | Offline |
| Accessibility | Easily accessible | Low accessibility |
| Tangibility | Software-based wallets; so, intangible | Physical wallets; so, tangible |
| Types | Mobile, web or desktop wallets | Paper or hardware wallets |
| Safety | Prone to hacking and attacks. So, less secure. | Less threat from hacking and attacks. So, more secure |
| Convenience | Easy and convenient | Less convenient |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Usability | Best to store a small amount of crypto | Best to store large amounts of cryptocurrency |
Hot and cold wallet setup
Although using a hot wallet for transactions is easy and convenient, it cannot be used to keep a large number of cryptocurrencies due to security threats. It is advisable to store your large amount of cryptocurrencies in cold wallets as they are the least vulnerable to security threats, such as malware attacks and phishing.
One important way of setting up wallets to avoid risks is to combine both hot and cold wallets, which reduces your funds’ online exposure. In this, each wallet is set up for different purposes. The hot wallets serve as the receiving wallet and sending wallet. The receiving wallet will manage the funds coming to the exchange, while the sending wallet will be used to send cryptos for transactions and trade.
As both the sending and receiving wallets will be hosted on online servers, the number of funds kept in both wallets should be minimized to reduce the risks of crypto vulnerability. The rest of the cryptos should be stored in your cold wallet. Doing this can ensure that most of your asset is safe in case of any security compromises.
How does hot and cold wallet interact?
As all of the funds that are transferred to you come to your receiving wallet, there are chances of crypto accumulation in your receiving wallet, resulting in crypto vulnerabilities. So, you need to send most of it to the cold wallet and some to the sending wallet. You need to have a minimum amount in your receiving wallet to transfer to the sending wallet once it falls short of cryptos, and this ensures that the sending wallet has enough cryptos whenever needed. However, suppose funds are not reliably coming to the receiving wallet, and the sending wallet urgently needs currencies. In that case, you can transfer the required amount from the cold wallet to the sending wallet.
How to mitigate crypto vulnerability?
Assume that you have a total of 200 ETH in your possession, and at any time, you want to avoid risking more than 30% of your funds. Based on this calculation, you need to set maximum and minimum thresholds per wallet to reduce the severity of any malware attack. So, the receiving wallet should have a minimum of 10 ETH and a maximum of 20 ETH. Similarly, the sending wallet should possess at least 20 ETH and up to 40 ETH. The rest of your assets should be kept in the cold wallet.
If you set a threshold for your sending and receiving wallets, adhere to it and ensure that the set amount does not exceed or drop down the limit. Excess funds are prone to vulnerabilities, and you cannot produce the required amount when needed if it is below the limit. So, always maintain an adequate amount of funds
How do hot and cold wallet setups in big systems work?
Hot and cold wallet setups vary, and each setup is designed based on the developer’s requirements and thought process. Through the following infographics, let us understand how hot and cold wallet setups are designed in big systems.
In the above-given infographic, if a person wants to send x number of tokens to another user, they input a request in the front end of the application, which is fetched in the API layer or the backend of the app. The backend transfers the input request to the wallet server. In a typical wallet architecture, a wallet server handles multiple microservices like managing nodes, databases, APIs or transaction services. As the user input, in this case, is related to the transaction service, the request is sent to this microservice.
The transaction service then sends the request to the wallet microservices, which handle all services related to the wallet. The wallet microservices can vary from platform to platform. In the above infographic, the wallet microservices include the following:
- Fund management for the hot wallet – It ensures that it always sticks to its threshold without crypto overflow or deficit to prevent risk exposure.
- Whitelisted IPs – It limits the number of people who can access your domain or server to a few trusted IP addresses permitted by you.
- Token – It manages and keeps track of your tokens, like x number of ETH or x number of SOL.
- Service monitoring – This microservice checks whether all services are working without glitches.
- Thresholds – These ensure that you have the required amount in your wallet or not to send it to others.
- 2-step authentication – It is a security process where you have to verify your identity twice before accessing the wallet ecosystem.
- Notifications – It alerts users on important matters like successful transaction completion notifications.
- KMS – Key management system or KMS helps create, store, and manage it safely.
- Rotate hot wallet
When the transaction input is transferred from the transaction service to the wallet microservices, all of the above microservices are carried out. Once all the services are done, and it is ascertained that your hot wallet has enough number of tokens, the x number of tokens is sent to the receiver. The transaction is, then, said to be successfully completed.
Conclusion
Merging both hot and cold wallets can help mitigate the risk of crypto attacks for both the users and the service providers. It acts as a comfortable middle ground by offering the benefits of both wallets, where one is used for crypto trading, and the other is used to hold the cryptos safely. Even though only hot wallets were popular during the initial days of crypto emergence, usage of cold wallets is getting more popular these days. Moreover, blending hot and cold wallets is gradually gaining prominence among crypto experts and service providers, owing to its huge benefits. Using just one wallet is, thus, outdated, and people gradually realize the advantages of combining both hot and cold wallets as an additional security measure.
Start a conversation by filling the form
All information will be kept confidential.
Insights
Stellar-vs-EVM-Based-Blockchains
Stellar and EVM-based blockchains are decentralized, open-source platforms designed to develop smart contracts and decentralized applications.
A deeper look into liquidity pools and how they are vital to the DeFi ecosystem
A liquidity pool is a group of digital assets gathered to facilitate automated and permissionless trading on the decentralized exchange platform.
What are Soulbound Tokens, and How do they Work?
Soulbound tokens, or SBTs, are digital identity tokens representing a person or entity’s features, traits and achievements. Learn more about SBTs.