AI in cybersecurity: Use cases, implementation, solution and development
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, enterprises are confronted with a new reality – The size and intricacy of potential threats have grown to a point where human capabilities alone are insufficient to deal with them effectively. The traditional notion of security, confined to human oversight, is no longer sufficient. Instead, businesses grapple with an ever-expanding attack surface, encompassing hundreds of billions of dynamic signals, each representing a potential point of vulnerability. This paradigm shift underscores the formidable challenges organizations face in safeguarding their systems and data from a vast array of constantly evolving security risks. What was once a puzzle, solvable with enough human diligence, has transformed into an intricate web of risk and uncertainty.
What’s the implication of this expansion? Cybersecurity has now transcended the limits of human cognition.
Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), technologies that are at the forefront when it comes to enhancing and strengthening digital security. These technologies have the ability to thoroughly examine millions of digital activities and pinpoint potential threats, whether they are zero-day vulnerabilities or insidious behavioral anomalies that precede phishing attacks.
The adaptability of AI is astounding. It evolves, learns, and builds profiles, turning historical data into a wealth of insight for preempting future breaches. It’s an arms race where cybercriminals constantly refine their tactics, leveraging resources like sophisticated language models to devise malicious code. The ease of access to such tools is, in part, what accelerates the menace of cybercrime today.
But businesses are rising to the challenge.
With a whopping 76% of companies earmarking AI and ML in their IT expenditures, the reliance on automation isn’t just a trend; it’s an integral and accelerating transformation shaping the landscape of modern business operations. The projected data overflow of 79 zettabytes by 2025 would be inconceivable to tackle manually, driving the need for intelligent, automated defenses.
Recent studies echo this sentiment, showcasing the committed investment in AI-driven security solutions. Blackberry’s latest findings revealed that 82% of IT leaders aim to enhance their cybersecurity arsenals with AI within the next two years, with nearly half planning to do so before the end of 2023.
The digital realm demands vigilance and innovation, and AI in cybersecurity is no longer an option—it’s an essential weapon in the ongoing battle against cybercrime.
In this article, we will explore the pivotal role that AI plays in fortifying digital defenses, its applications in threat detection and response, and the transformative impact it has on safeguarding sensitive data and systems in an increasingly interconnected world.
- What is AI in cybersecurity?
- How does AI address current cybersecurity challenges?
- What AI can do for cybersecurity?
- AI for cybersecurity: Popular use cases
- Streamlining cybersecurity workflow with GenAI
- How AI and ML are transforming endpoint security?
- How to implement AI in cybersecurity?
- How does LeewayHertz’s generative AI strengthen organizational cybersecurity?
- LeewayHertz’s AI development services for cybersecurity
- The role of machine learning and deep learning in cybersecurity
- How is AI used in cybersecurity? A detailed breakdown of the process
- How are enterprises leveraging AI in cybersecurity?
- Benefits of AI in cybersecurity
What is AI in cybersecurity?
AI is transforming cybersecurity by utilizing sophisticated algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data sourced from various organizational channels. These channels encompass user behavior logs, network traffic patterns, and system configurations. Through this analysis, AI systems establish a baseline of normal behavior for the organization’s digital environment.
Once this baseline is established, AI algorithms continuously monitor systems and networks for deviations from the norm. These deviations, termed anomalies, are potential security threats or breach indicators. AI systems swiftly detect anomalies in real time and flag them for further scrutiny by cybersecurity professionals.
While AI plays a pivotal role in cybersecurity, human expertise remains indispensable. AI systems aid cybersecurity professionals by automating mundane tasks, identifying potential threats, and offering insights. Nevertheless, human intervention is often imperative to interpret AI-generated alerts, investigate security incidents, and formulate effective threat mitigation and response strategies.
AI also plays a crucial role in endpoint security, a vital component of cybersecurity. Organizations can detect and prevent threats targeting individual devices such as computers, smartphones, and IoT gadgets by employing AI algorithms. These AI-driven endpoint security solutions analyze device behavior and network traffic patterns to identify and mitigate potential threats in real time. Furthermore, AI enhances incident response capabilities by automating remediation actions and providing valuable insights for proactive threat management. Thus, AI integration in endpoint security strengthens overall cybersecurity posture, ensuring comprehensive protection across all organizational devices.
How does AI address current cybersecurity challenges?
Expanded attack surface
Challenge: With the proliferation of internet-connected devices and platforms, the attack surface has significantly widened. This provides cybercriminals with more opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities, posing a challenge for security professionals to defend every entry point effectively.
Solution: AI-driven threat detection systems can continuously monitor and analyze network traffic, endpoints, and cloud environments. Their objective is to identify abnormal behavior and potential security threats. These systems can detect anomalies and proactively respond to threats in real time, helping organizations safeguard against attacks on various entry points.
Device proliferation
Challenge: Modern organizations rely on many devices, including computers, smartphones, and IoT devices. Managing and securing each device poses a complex task, requiring continuous monitoring and adaptable security measures to keep pace with evolving threats.
Solution: AI endpoint security solutions can provide comprehensive device management and threat detection capabilities across all devices, including computers, smartphones, and IoT devices. These solutions can automatically detect and patch vulnerabilities, enforce security policies, and identify/respond to malware and other threats. Consequently, they streamline the management and security of various devices across the organization.
Diverse attack methods
Challenge: Cybercriminals employ various attack techniques, from phishing and ransomware to zero-day exploits. This diversity complicates the security landscape, necessitating a comprehensive defense strategy and specialized knowledge to combat each threat effectively.
Solution: AI can analyze large amounts of data from disparate sources to identify patterns and indicators of various cyber attacks, including phishing attempts, ransomware, and zero-day exploits. By leveraging ML and behavioral analysis techniques, AI-powered security systems can adapt and evolve to detect and mitigate new and emerging threats, enhancing the organization’s defense against diverse attack methods.
Shortage of cybersecurity experts
Challenge: The growing demand for cybersecurity expertise has resulted in a shortage of skilled professionals. Organizations need help finding people who can monitor security systems and respond to cyber threats. As a result, defending against attacks becomes even more difficult.
Solution: AI-driven security automation tools can augment the capabilities of existing cybersecurity teams by automating repetitive tasks, such as threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management. These tools bridge the gap between the demand for cybersecurity expertise and the need for more skilled professionals by enabling organizations to do more with limited resources and empowering existing staff to focus on higher-value tasks.
Overwhelming data volumes
Challenge: In the era of big data, organizations generate and collect vast amounts of information daily. Analyzing this data exceeds human capacity, making identifying meaningful patterns and insights difficult. AI-driven solutions are necessary to efficiently detect anomalies and potential threats amidst this overwhelming volume of data.
Solution: AI and machine learning technologies can process and analyze large volumes of data from various sources to identify anomalies, trends, and potential security threats that may go unnoticed by human analysts. Using advanced analytics and anomaly detection algorithms, AI-powered security systems can efficiently sift through massive amounts of data to identify and prioritize security events, allowing organizations to detect and respond to threats more effectively.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
What AI can do for cybersecurity?
AI’s capabilities extend far beyond human capacity, offering innovative solutions to address the complex challenges of modern cybersecurity. Here, we will explore the transformative role of AI in enhancing digital security, from mitigating human errors to streamlining threat response and predicting emerging threats. And as we delve into the implications of integrating machine learning and AI into security systems, it’s crucial to understand the existing challenges in cybersecurity and how AI addresses them.
Addressing human errors in cybersecurity configuration
Human error plays a substantial role in creating vulnerabilities within cybersecurity. Ensuring proper system configuration can be an intricate and demanding task, even for extensive IT teams actively involved in the setup. With the continuous evolution of technology, security measures have become increasingly complex and multifaceted. Implementing responsive tools could assist teams in identifying and rectifying issues that emerge when network systems undergo changes, upgrades, or replacements.
Take, for example, the integration of contemporary internet structures like cloud computing with legacy local frameworks. IT professionals must guarantee compatibility within enterprise environments to fortify these mixed systems. The manual evaluation of configuration security leads to exhaustion as teams juggle never-ending updates along with routine daily responsibilities. By applying intelligent and adaptive automation, teams could receive prompt guidance on newly detected problems and insights into potential solutions. Some systems may even be designed to automatically modify settings as required, enhancing efficiency and reducing the risk of human error.
Boosting efficiency in repetitive cybersecurity tasks
Human efficiency in performing repeated activities is a critical issue in the cybersecurity field. The manual processes in setting up an organization’s multiple endpoint machines can be incredibly time-consuming and rarely executed perfectly. Even after the initial setup, IT teams frequently have to revisit the same machines to correct misconfigurations or update outdated setups that are not amendable to remote patching.
Moreover, when faced with the need to respond to security threats, unexpected complications can delay human reactions. The ever-changing nature of such threats demands a rapid response that human teams might find challenging to achieve. Here, a system that leverages AI and machine learning can significantly enhance efficiency, adapting quickly to new information and evolving threats without delays hindering a human response. Such an approach streamlines the process and ensures a more consistent and robust defense against potential cybersecurity threats.
Reducing alert fatigue in cybersecurity
The challenge of threat alert fatigue is a significant weakness within organizations, as it can overwhelm cybersecurity personnel. The number of alerts for known issues can multiply rapidly with the increasing complexity of security layers. These constant notifications require human teams to analyze, make decisions, and take appropriate actions.
This flood of alerts can lead to decision fatigue, a daily struggle for cybersecurity professionals. Ideally, they would proactively address these threats and vulnerabilities, but many teams are constrained by time and staffing, often having to prioritize major concerns over secondary ones.
Integrating AI into cybersecurity efforts can alleviate this issue by enabling IT teams to handle more threats efficiently. Automated labeling can streamline the process, allowing for easier management of threats. Additionally, some concerns may even be directly addressed by machine learning algorithms, further reducing the burden on human teams.
Reducing threat response time in cybersecurity
Threat response time is a critical factor in evaluating the effectiveness of cybersecurity teams. In the past, malicious attacks often required careful planning and execution, sometimes taking weeks to unfold. However, with technological advancements, even threat actors have benefited from automation, leading to quicker attacks like the recent LockBit ransomware; some taking as little as thirty minutes.
This rapid pace can cause human responses to fall behind, even when dealing with familiar types of attacks. As a result, many teams find themselves reacting to successful attacks rather than preventing attempted ones, while undiscovered attacks present their own unique dangers.
Machine learning can offer a valuable solution to this problem. Using ML-assisted security, data from an attack can be quickly grouped and prepared for analysis, providing cybersecurity teams with concise reports to streamline decision-making. More than just reporting, this advanced security approach can also suggest actions to mitigate further damage and avert future attacks, thus significantly reducing threat response time.
Identifying and predicting new threats in cybersecurity
Identifying and predicting new threats is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity, impacting the time it takes to respond to cyber-attacks. With known threats already causing delays, unfamiliar attack types, behaviors, and tools can further slow down response times. Quieter threats, such as data theft, may even go unnoticed.
The ever-evolving nature of attacks, leading to zero-day exploits, poses a constant concern within network defense. On the positive side, cyber-attacks are seldom entirely new; they often build upon previous attacks’ behaviors, frameworks, and source codes. This provides machine learning with an existing pattern to analyze.
ML-based programming can detect common features between new and previously recognized threats, something humans might struggle to accomplish promptly. This reinforces the need for adaptive security models. By employing machine learning, cybersecurity teams can more easily anticipate new threats, reducing the response lag time due to enhanced threat awareness.
Managing staffing capacity in cybersecurity
Staffing capacity continues to challenge many IT and cybersecurity teams worldwide. Finding qualified professionals may be difficult depending on an organization’s particular needs. Hiring human help can consume a significant portion of a budget, even when possible. Beyond daily wages, supporting staff involves continuous investment in education and certification, as staying up-to-date in cybersecurity requires constant learning and adaptation.
AI-based security tools offer an alternative that can ease these burdens. By incorporating AI and machine learning, a leaner team can effectively manage security, reducing both cost and staffing requirements. While team members will still need to stay current with emerging AI and machine learning trends, the overall financial and time savings can make this an appealing option for many organizations. This approach addresses the staffing capacity issue and aligns with the continuous innovation that characterizes the cybersecurity field.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
AI for cybersecurity: Popular use cases
In cybersecurity, AI plays a crucial role in the real-time identification of and response to cyber threats. By utilizing sophisticated algorithms, AI can sift through vast volumes of data to recognize patterns that signal the presence of a cyber threat.
Malware detection
Malware poses a serious risk to cybersecurity, and traditional detection methods often rely on signature-based techniques that identify known malware variations. However, these methods only work on recognized threats and can be easily circumvented by slightly altered malware.
AI-driven malware detection offers a more advanced solution, utilizing machine learning algorithms to detect and counter both known and unknown malware threats. These algorithms can analyze vast data to discover patterns and irregularities that might elude human analysts.
By examining malware behavior, AI can pinpoint new and unfamiliar malware variations, something that traditional antivirus software might overlook. AI-based detection methods can be taught using labeled data (data with specific attributes such as malicious or benign tags) and unlabeled data (data without specific tags), which helps identify patterns and anomalies.
Various techniques are employed in AI-driven malware detection, including static analysis, which investigates a file’s attributes such as size, structure, and code, and dynamic analysis, which observes the file’s behavior upon execution. These methods make AI-based solutions more sophisticated and effective in malware detection, outperforming traditional antivirus software in identifying new and hidden threats.
Phishing detection
Phishing, a common cyber-attack method targeting individuals and organizations, has historically been combated with rules-based filtering or blacklisting to identify and block known threats. However, these traditional methods only work on recognized attacks, often missing new or modified phishing strategies.
AI-driven phishing detection offers a more dynamic solution, employing machine learning algorithms that analyze an email’s content and structure to detect potential phishing attempts. These algorithms can learn from extensive data, identifying patterns and inconsistencies that signal a phishing attack.
Furthermore, AI-based phishing detection goes beyond mere content analysis. It can also study user behavior, such as clicking on suspicious links or inputting personal information in response to a phishing email. If such activity is detected, the AI system can flag it, alerting security teams.
Security log analysis
Traditional methods of security log analysis, relying on rule-based systems, have inherent limitations in identifying new or evolving threats. These conventional approaches may miss critical warning signs, resulting in delayed breach responses.
In contrast, AI-based security log analysis deploys machine learning algorithms to handle vast amounts of real-time security log data. These algorithms are trained to recognize patterns and inconsistencies that might signal a breach, even without a known threat signature, allowing organizations to act swiftly.
One of the unique strengths of AI-based log analysis is its ability to identify potential insider threats. By scrutinizing user behavior across various systems and applications, AI can detect abnormal actions, such as unauthorized access or unusual data transfers, that may hint at an insider threat. This allows organizations to intercept potential breaches proactively.
Network security
AI-enhanced network security leverages algorithms trained to monitor for abnormal activity, recognize unusual traffic patterns and pinpoint devices unauthorized to access the network.
Through anomaly detection, AI analyzes network traffic to discern patterns that deviate from the norm. By studying historical traffic data, these algorithms can understand a network’s regular activity and flag anomalies like unexpected port or protocol usage or traffic from suspicious IP addresses.
Furthermore, AI contributes to network security by vigilantly monitoring devices connected to the network. It can identify devices the IT department hasn’t authorized and mark them as potential security risks. The AI system can alert security teams to examine the situation if a new or unfamiliar device is detected on the network. This includes watching the behavior of devices for uncommon activity patterns, a method that offers another layer of protection against potential threats.
Endpoint security
Endpoints like laptops and smartphones are common targets for cybercriminals, and traditional security measures often fall short. AI-based endpoint security solutions fill this gap by employing machine learning algorithms that analyze endpoints’ behavior to detect known and unknown threats.
Unlike traditional signature-based detection, which only recognizes known malware, AI can identify new and modified malware by scrutinizing its actions. This includes scanning files for malicious content, quarantining suspicious files, monitoring endpoint activities for abnormal patterns, and blocking unauthorized access attempts to secure sensitive data.
One standout feature of AI-based endpoint security is its ability to adapt and grow continuously. As cyber threats become more intricate, AI algorithms can absorb new information, identifying novel patterns and threats, thus offering enhanced protection against evolving dangers that traditional software might miss.
The real-time monitoring capability of AI-based endpoint security also sets it apart. Observing endpoint behavior as it occurs and alerting security teams promptly enables a rapid response to threats, minimizing potential harm.
Breach risk prediction
The machine learning model offers a comprehensive and sophisticated approach to breach risk prediction by utilizing a blend of existing techniques through a cognitive learning framework. This method encompasses monitoring access points, both password and biometric-based, and employs AI algorithms to recognize authorized users.
If unauthorized access is detected, the system triggers an alert and disables the current access point. In case of a remote hacking attempt, the model creates additional protective layers based on the type of attack, leveraging honeypot technology to identify the attack type at an early stage.
The model can trace the hacker’s IP address using the tracert/traceroute command method. If the defense mechanisms are overcome, the system disconnects from the network as a last resort and utilizes SHA3 hashing to provide a secure means for the user to regain access.
This comprehensive approach, emphasizing dynamic adaptation and secure recovery processes, provides robust protection against cybersecurity threats, including the ability to anticipate attack types and respond effectively.
User authentication
Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning in user authentication represents a significant leap from traditional methods, offering enhanced security while maintaining user convenience. Gone are the days when passwords, PINs, and security questions sufficed; these are often susceptible to breaches. In their place, AI and ML provide more sophisticated solutions.
Biometric authentication, using distinct physical or behavioral attributes such as fingerprints, facial characteristics, or voice patterns, is a notable development in this realm. For example, facial recognition systems use AI to evaluate myriad facial aspects, forming a unique ‘faceprint.’ ML algorithms then match this with stored information for user verification. This amplifies security and simplifies the process, requiring nothing more than the user’s face.
The innovation doesn’t stop there; behavioral biometrics employ AI and ML to analyze a person’s specific behavioral traits, such as typing style or touch-screen interactions. These algorithms adapt and recognize these patterns, offering uninterrupted, ongoing authentication.
Furthermore, AI and ML enrich multi-factor authentication by assessing various elements like location, device, and time, triggering additional authentication steps if a login attempt seems risky. This responsive system adds an essential layer of protection.
Even the threat of deepfakes, where one’s appearance can be artificially replaced, is being countered with AI and ML. These technologies can detect such fraudulent attempts, ensuring the credibility of biometric verification.
Spam filtering
Artificial intelligence, specifically machine learning, plays a crucial role in bringing about significant changes and improvements in the field of spam filtering within the realm of cybersecurity. Companies like Google are leveraging technologies like TensorFlow to intercept a staggering 100 million spam emails daily, moving from mere pattern recognition to self-evolving and optimizing systems.
Machine learning approaches offer multiple methods for detecting and filtering spam. Keyword and content-based filtering utilize algorithms such as Naïve Bayesian classification, and k-nearest neighbor (kNN) to evaluate keywords, phrases, and their email distribution to create rules that help in spam identification.
Similarity-based filtering employs kNN to categorize emails based on their resemblance to previously stored emails. Attributes of these emails are used as foundational criteria, and new instances are mapped as reference points for incoming emails.
Sample-based filtering involves training machine learning algorithms on both legitimate and spam samples to determine whether new emails should be classified as spam or not. This process ensures that the system learns from real-world examples.
Adaptive email spam filtering takes a unique approach by grouping spam emails and representing each group with specific tokens or emblematic texts comprising words, phrases, or even nonsensical strings. Incoming emails are then compared to these representative texts to decide their classification.
Its ability to adapt and enhance its performance over time makes AI highly effective in spam filtering. This adaptability ensures a robust and evolving defense against spam, fulfilling both individual needs and business security requirements.
Password protection
Within the realm of cybersecurity, Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as a formidable ally in enhancing password protection. At its core, AI harnesses machine learning algorithms to bolster the security of passwords through various mechanisms and processes.
Pattern recognition: AI systems diligently sift through extensive databases of previous password breaches, identifying recurring patterns associated with weak or easily compromised passwords. Leveraging this insight, AI empowers users to create robust and resilient passwords by providing tailored recommendations.
AI-driven password managers: AI-enabled password managers offer a multifaceted approach to security. They generate intricate, unique passwords for every account, diminishing the risk of password reuse. Furthermore, these managers commonly encompass advanced security features like two-factor authentication (2FA) for an additional layer of defense.
Continuous threat vigilance: AI-powered systems engage in real-time monitoring of login activities, constantly on the lookout for anomalies. Whenever a user’s login behavior significantly deviates from their established patterns, the AI system raises an alert, swiftly detecting and notifying users about potential unauthorized access attempts.
Behavioral biometrics: AI introduces an innovative dimension through the integration of behavioral biometrics. Elements like keystroke dynamics and mouse movements are harnessed to uniquely authenticate users based on their distinctive interaction patterns, providing an added layer of safeguarding beyond conventional password practices.
Adaptive authentication: AI seamlessly implements adaptive authentication strategies, where the required level of security varies contingent upon risk factors. For instance, when a login attempt is perceived as originating from an unfamiliar device or location, the AI system may prompt users to undergo additional verification measures.
Password recovery with AI chatbots: Password recovery, often a cumbersome process, becomes streamlined and secure with AI-driven chatbots. These virtual assistants can efficiently verify user identity through a series of questions or biometric data, ensuring a secure recovery process.
Harnessing threat intelligence: AI systems access comprehensive threat intelligence databases to ascertain if a user’s password has previously been compromised in past breaches. In such cases, the AI system promptly alerts the user, urging an immediate password change.
AI emerges as a pivotal force in password protection, not merely fortifying password complexity but also offering continuous monitoring, adaptive security protocols, behavioral authentication, and a seamless recovery process. This multifaceted approach positions AI as an indispensable asset in fortifying cybersecurity measures, assuring enhanced password security.
Bot identification
Artificial intelligence plays a significant role in protecting against malicious bots in the field of cybersecurity. AI’s role extends beyond just social bots, encompassing various applications to safeguard digital landscapes. Utilizing sophisticated techniques like machine learning, AI can detect and prevent bot-related threats by analyzing various attributes and behaviors.
One common method is graph-based detection, which differentiates between genuine user relationships and bot-driven connections. Crowdsourcing is another approach, leveraging human intelligence to discern patterns that indicate bot activity.
Machine learning is particularly instrumental in offering protection against bots. For instance, one empirical study collected labeled datasets of bots and human users on Twitter, categorizing them into different types of bots, such as social and traditional spambots. Attributes such as follower count, friends count, retweet count, reply count, the number of hashtags, shared URLs, screen name, user ID, and even the sentiment of a tweet’s text were analyzed to distinguish bots from human users. Algorithms such as Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and Logistic Regression were employed, with Random Forest showing promising results as a potent model for bot detection.
These advancements in AI and machine learning aid in detecting and blocking malicious bots and offer insights into their operational dynamics. While bots can have legitimate applications, such as in marketing or political campaigning, their potential misuse necessitates robust detection mechanisms. By employing AI for bot protection, the cybersecurity landscape can adapt and respond to evolving threats, safeguarding against the malicious use of bots and curbing the spread of digital misinformation. The application of machine learning and discourse analysis further enhances the ability to pinpoint and neutralize bot activity, contributing to a more secure and trustworthy digital environment.
Behavioral analysis
The evolution of AI and machine learning in cybersecurity has significantly shifted the focus from merely detecting known malicious signatures to analyzing complex behavioral patterns. In the past, cybersecurity mechanisms were designed to recognize the execution of specific malicious programs, giving birth to the antivirus industry. However, as cybercriminals have become more adept at changing their behavior to evade detection, the importance of behavioral analysis in cybersecurity has grown.
AI and machine learning are now tasked with observing and understanding several key areas of behavior. Endpoint behavior analysis focuses on the actions taken by malware on an individual system, such as file writing, process launching, and resource accessing, including the more covert tactics used in fileless attacks. This approach can discern abnormal actions that contrast with standard operations like opening a Word document or a web browser.
Examining network behavior involves tracking predictable patterns in network traffic, such as the interaction with specific sites or systems, data transfer, and encryption use. Any deviations from these norms, like abnormal use of ports or unusual data amounts, can indicate malicious activity, such as command-and-control servers orchestrating an attack.
User behavior analysis considers the regular actions of users, such as login times, application usage, and data interactions. Any variations from these routines, like unusual login times or abnormal application usage, may signify a compromised account or endpoint.
Streamlining cybersecurity workflow with GenAI
Generative AI is rapidly transforming cybersecurity, evolving defense strategies from reactive measures to proactive threat neutralization. From predicting emerging vulnerabilities and generating sophisticated phishing simulations to automating incident response and fortifying security awareness training, GenAI is empowering security professionals to outsmart cyber threats with speed and precision.
Here are some of the personas that may be involved in cybersecurity workflow:
- SOC analyst: Monitors security systems, analyzes events, and responds to incidents, acting as the front line of defense.
- Security administrator: Manages and maintains security systems, ensuring their effectiveness and compliance with policies.
- Incident responder: Swiftly contains and mitigates security breaches, following established protocols to minimize damage.
- Security analyst: Conducts in-depth threat analysis, hunts for hidden threats, and collaborates with GenAI to uncover vulnerabilities.
- Security compliance officer: Ensures adherence to regulations and best practices, maintaining a secure and compliant environment.
Here’s how GenAI is making a significant impact across the entire cybersecurity lifecycle:
- Threat prediction and prevention
| Steps involved | Sub steps | Role of GenAI |
| Threat and vulnerability assessment |
|
|
| Security posture optimization |
|
|
| Validation and continuous improvement |
|
|
- Real-time threat management
| Steps involved | Sub steps | Role of GenAI |
| Incident detection and analysis |
|
|
| Containment and eradication |
|
|
| Recovery and remediation |
|
|
| Continuous learning and improvement |
|
|
- Post-incident actions
| Steps involved | Sub-steps | Role of GenAI |
| Threat containment |
|
|
| Threat mitigation and recovery |
|
|
| Post-incident review and improvement |
|
|
- Continuous improvement and adaptation
| Steps involved | Sub steps | Role of GenAI |
| Data collection and analysis |
|
|
| Strategy evolution and automation |
|
|
| Evaluation and continuous improvement |
|
|
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
How AI and ML are transforming endpoint security?
Traditional endpoint security solutions have long relied on signature-based detection, which identifies known threats and blocks them. However, this approach is becoming less effective against evolving cyber threats. Integrating AI in endpoint security solutions into your cybersecurity stack can greatly enhance your ability to detect anomalous behavior and identify previously unknown threats. Machine learning algorithms enable users to uncover threats that may otherwise go unnoticed. Here is how integrating AI in endpoint security can transform it:
- Automated threat detection & response: AI brings the power of automation to endpoint security, enabling critical security functions such as patch management, anomaly detection, and secure authentication mechanisms to be automated. Imagine quickly analyzing attack characteristics and remedying them in record time. AI can distinguish normal activity from anomalies, reducing the time to action and remediation. Ultimately, this can lead to fewer successful cybersecurity infiltrations.
- Remediation with predictive analytics: AI empowers endpoint security through predictive analytics, enabling organizations to analyze historical data and diverse datasets specific to endpoint activities. This capability allows organizations to forecast potential threats and establish patterns indicative of malicious behavior. By gaining deeper visibility and insights into endpoint security postures, organizations can proactively identify and mitigate risks before they escalate, enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience at the endpoint level.
- Knowledge consolidation: Effective endpoint protection relies on collecting and analyzing vast information. Unified security and endpoint management practices are becoming more prevalent, but it’s essential to consolidate data from various sources to identify potential blind spots. AI can synthesize and transform unstructured data into structured data, providing valuable insights for analysis. Organizations can analyze every action by collecting more information from endpoint users without compromising their privacy, leaving cybercriminals with fewer opportunities to compromise endpoints.
- Malicious file and process identification: Using AI in endpoint security solutions involves analyzing data to identify malicious files or processes. By learning from past incidents, they can detect patterns indicative of malware or other cyber threats, bolstering defense mechanisms specifically tailored for endpoint security.
- Sandbox analysis: AI in endpoint security protection software often includes sandboxing capabilities, which isolate suspicious applications or files in a controlled environment for analysis. This helps identify and neutralize potential threats without risking the entire system’s security.
- Ransomware protection: AI in endpoint security solutions can revert endpoints and data to a previous secure state, effectively minimizing the impact of the attack and restoring normal operations.
- Behavioral analysis: It entails monitoring user behavior to detect anomalies that could signal a potential threat. For instance, if a user suddenly accesses sensitive files at unusual times or from unusual locations, it could indicate a compromise. ML algorithms can be trained to recognize these patterns and alert security teams when suspicious behavior is detected.
- Threat hunting: Threat hunting is a proactive approach that involves actively searching for hidden threats within a network or system. Whereas endpoint security is a preventive measure.
AI and ML are transforming endpoint security by enabling more advanced threat prevention techniques, efficient incident response, cost-effective solutions, and scalability. These technologies analyze patterns and anomalies in user behavior and network traffic to proactively identify and prevent cyber attacks. By providing real-time insights and automating repetitive tasks, AI and ML help security teams respond to incidents more effectively, freeing up personnel for critical tasks. Moreover, automation reduces the cost of endpoint security by minimizing human intervention, saving time and money. Additionally, AI and ML can scale to analyze large volumes of data from multiple endpoints, ensuring comprehensive protection in complex IT environments.
How to implement AI in cybersecurity?
Implementing AI in cybersecurity involves several key steps:
- Assessment of needs: Begin by assessing your organization’s cybersecurity needs and identifying areas where AI can make a significant impact. This could include threat detection, incident response, vulnerability management, or user behavior analysis.
- Data collection and preparation: Gather relevant data, such as system logs, network traffic, security alerts, and threat intelligence feeds. Ensure that the data is clean, organized, and properly labeled for training AI algorithms.
- Selection of AI technologies: Choose the appropriate AI technologies and algorithms based on your specific cybersecurity requirements. This may include machine learning, natural language processing, deep learning, or neural networks.
- Model training: Train your AI models using labeled datasets to recognize patterns, anomalies, and potential threats. Continuously refine and update your models as new data becomes available to improve accuracy and effectiveness.
- Integration with security infrastructure: Integrate AI-powered cybersecurity solutions into your existing security infrastructure. This may involve deploying AI-enabled endpoint protection, network security, or security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
- Testing and validation: Thoroughly test and validate your AI models and cybersecurity solutions in a controlled environment before deployment. Evaluate their performance, accuracy, and effectiveness against various types of cyber threats.
- Deployment and monitoring: Deploy AI-powered cybersecurity solutions across your organization’s network and endpoints. Monitor their performance in real-time, and fine-tune their configurations as needed to adapt to evolving threats and security challenges.
By following these steps, organizations can successfully implement AI in cybersecurity to enhance threat detection, response capabilities, and overall security posture. LeewayHerts is a leading AI development company specializing in building cybersecurity solutions. Our innovative AI solutions empower organizations to empower their defense against evolving cyber threats. With a focus on innovation and expertise in AI algorithms, we deliver tailored cybersecurity solutions that safeguard your digital assets effectively.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
How does LeewayHertz’s generative AI strengthen organizational cybersecurity?
LeewayHertz’s generative AI platform, ZBrain, plays a transformative role for organizations aiming to enhance and fortify their cybersecurity defenses. As a comprehensive, enterprise-ready platform, ZBrain empowers businesses to design and implement applications tailored to their specific operational requirements. The platform uses clients’ data, whether in the form of text, images, or documents, to train advanced LLMs like GPT-4, Vicuna, Llama 2, or GPT-NeoX for developing contextually aware applications capable of performing diverse tasks.
Within the dynamic business landscape, enterprises often grapple with challenges like ever-evolving security threats, persistent vulnerabilities, and the imperative for swift action. ZBrain effectively addresses these challenges through its distinctive feature called “Flow,” which provides an intuitive interface that allows users to create intricate business logic for their apps without the need for coding. Flow’s easy-to-use drag-and-drop interface enables the seamless integration of large language models, prompt templates, and media models into your app’s logic for its easy conceptualization, creation, or modification.
To comprehensively understand how ZBrain Flow works, explore this resource that outlines a range of industry-specific Flow processes. This compilation highlights ZBrain’s adaptability and resilience, showcasing how the platform effectively meets the diverse needs of various industries, ensuring enterprises stay ahead in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
ZBrain apps empower organizations by significantly contributing to proactive risk mitigation, improved decision-making, and heightened cybersecurity resilience while adhering to rigorous data privacy standards. This leads to the swift identification of threats, enhancement of incident response mechanisms, and the elevation of cybersecurity measures, resulting in improved operational efficiency and safety.
LeewayHertz’s AI development services for cybersecurity
At LeewayHertz, we design customized AI solutions that address the unique demands of cybersecurity. We offer strategic AI/ML consulting to help organizations harness AI for enhanced threat detection, improved incident response, and optimized security operations.
Our proficiency in developing Proof of Concepts (PoCs) and Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) allows organizations to evaluate the real-world impact of AI tools, ensuring solutions are both effective and tailored to the cybersecurity sector’s specific needs.
Our expertise in generative AI transforms routine tasks like threat monitoring and incident reporting, automating these processes to free up security teams for more strategic roles.
By fine-tuning large language models to the specific terminology and intricacies of cybersecurity protocols and network behaviors, LeewayHertz enhances the accuracy and relevance of AI-driven communications and analyses.
Additionally, we ensure these AI systems integrate seamlessly with existing technological infrastructures, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making in cybersecurity operations.
Our AI solutions development expertise
AI solutions development for cybersecurity typically involves creating systems that enhance threat detection, automate incident response, and fortify network defenses. These solutions integrate key components such as data aggregation technologies, which compile and analyze security information from diverse sources. This comprehensive data foundation supports predictive analytics capabilities, allowing for forecasting security threats that guide strategic decisions. Additionally, machine learning algorithms tailor security measures to specific organizational vulnerabilities, ensuring that each system’s security framework is robust and adaptive. These solutions often cover real-time threat detection, risk assessment, regulatory compliance, and security posture management.
Overall, AI solutions in cybersecurity aim to optimize security outcomes, improve operational efficiency, and enhance the robustness of protection measures.
AI agent/copilot development for cybersecurity
LeewayHertz builds custom AI agents and copilots that enhance various cybersecurity operations, enabling organizations to save time and resources while facilitating faster and more effective decision-making. Here is how they help:
Threat detection and monitoring:
- Perform continuous network monitoring to detect unusual activities that could indicate threats.
- Analyze security logs across platforms to identify potential security breaches or vulnerabilities.
- Employ advanced pattern recognition to predict and identify emerging threats from global security feeds.
Incident response and management:
- Automate the initial analysis of security breaches, speeding up incident response times and mitigating potential damage.
- Prioritize incident response actions based on threat severity and potential impact.
- Coordinate and streamline response protocols to ensure quick restoration of normal operations.
Compliance and risk management:
- Automate the monitoring of compliance with cybersecurity standards and regulations.
- Integrate risk management practices to assess and prioritize organizational risks based on real-time data.
- Generate compliance reports automatically, ensuring accurate documentation and evidence for audits.
Process automation:
- Automate routine cybersecurity tasks such as patch management, vulnerability scans, and security audits.
- Enhance cybersecurity training programs by simulating real-world attack scenarios for training purposes.
- Streamline user and entity behavior analytics to detect insider threats and compromised accounts.
Cybersecurity analytics:
- Gather and analyze data from diverse sources to provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s security landscape.
- Provide actionable insights into security operations, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of cybersecurity measures.
Cybersecurity infrastructure management:
- Play a crucial role in monitoring and managing the health and performance of security infrastructure by analyzing large datasets, identifying potential hardware failures or capacity issues, and recommending proactive measures. They can also provide timely alerts and insightful reports to help security teams optimize infrastructure performance and mitigate risks.
- Automate the deployment of security updates and patches to maintain the integrity of systems and applications.
- Enhance network security configuration and management through automated policy enforcement and anomaly detection.
LeewayHertz’s AI agents and copilots not only increase the efficiency of cybersecurity processes but also significantly enhance the quality of threat detection and strategic decision-making. By integrating these advanced AI solutions into their existing infrastructure, organizations can achieve a significant competitive advantage, navigating the complex cybersecurity landscape with innovative, efficient, and reliable AI-driven tools and strategies.
The role of machine learning and deep learning in cybersecurity
Machine learning and deep learning have transformed the field of cybersecurity, bringing about a transformative shift in how threats are detected and managed. Here’s how they are applied.
Classification of data
Data classification is a key application of machine learning in cybersecurity. It operates by employing preset rules to categorize various data points. Labeling these specific points can establish an essential profile on different aspects such as attacks, vulnerabilities, and proactive security measures. This classification process is crucial to understanding and responding to threats, providing an essential bridge between machine learning algorithms and effective cybersecurity management.
Data clustering
Data clustering is another vital ML technique applied in cybersecurity. Unlike classification, clustering focuses on grouping data that deviates from preset rules into collections or “clusters” with shared attributes or peculiar characteristics. For instance, when a system encounters attack data it is not previously trained for, data clustering can be instrumental. By analyzing these clusters, security experts can figure out how an attack was carried out, identify what vulnerabilities were exploited, and uncover what information was potentially exposed. This approach enhances the understanding of unfamiliar threats and helps strengthen security measures against similar attacks in the future.
Suggesting recommended courses of action
In the realm of cybersecurity, machine learning plays a crucial role in elevating the effectiveness of security measures. It accomplishes this by providing valuable insights and recommendations for proactive actions that can be taken to safeguard digital systems and data. These recommendations are not born from autonomous AI making intelligent decisions but are formulated through an adaptive conclusion framework that analyzes behavior patterns and previous decisions. The system can deduce logical relationships and provide naturally suggested responses to threats by sifting through preexisting data points. This method assists significantly in threat response and risk mitigation, offering a more refined and efficient approach to addressing security concerns. It exemplifies how machine learning transcends traditional decision-making processes in cybersecurity, making it an indispensable tool in modern security strategies.
Utilizing possibility synthesis in cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, machine learning enables the concept of possibility synthesis. This approach allows for generating new possibilities or outcomes by drawing lessons from previous data and new, unfamiliar datasets. Unlike recommendations, possibility synthesis focuses more on evaluating the likelihood that a certain action or system state aligns with similar past scenarios. For instance, this method can preemptively probe and identify weak points within an organization’s systems. Cybersecurity professionals can better anticipate potential vulnerabilities and prepare more effective defenses by harnessing machine learning to synthesize possible outcomes. It showcases yet another innovative way machine learning can be harnessed to enhance cybersecurity practices.
Predictive forecasting
Predictive forecasting is a highly sophisticated and advanced aspect of machine learning used in the field of cybersecurity. By evaluating existing datasets, machine learning algorithms can anticipate potential outcomes. This forward-thinking approach is highly beneficial in several crucial areas:
- Building threat models: By analyzing historical data and previous attack patterns, predictive forecasting can create models that anticipate future threats. This enables security professionals to take preemptive measures to protect their systems.
- Outlining fraud prevention: Financial and online fraud can be predicted by examining trends and anomalies in transactional data. Machine learning can identify suspicious activities that deviate from established patterns, aiding in the early detection and prevention of fraud.
- Data breach protection: Data breaches often follow recognizable patterns. Using predictive forecasting, machine learning models can foresee potential breaches by identifying weak points and common tactics used by cybercriminals. This allows organizations to strengthen their defenses and reduce the likelihood of a successful breach.
- Predictive endpoint solutions: Many security solutions now incorporate predictive analytics to protect endpoints like computers and mobile devices. By understanding the behaviors typical of malware and other threats, these solutions can block attacks before they occur.
Predictive forecasting in cybersecurity is not just about predicting what might happen but also about enabling a more proactive defense strategy. Through continuous analysis and learning from existing data, machine learning facilitates the development of intelligent systems that can adapt and respond to an ever-changing threat landscape. It exemplifies how integrating machine learning with traditional security measures can create a more robust and resilient cybersecurity framework.
Machine learning and deep learning offer an advanced, dynamic approach to cybersecurity. It provides a robust defense mechanism through a combination of pattern analysis, specialized knowledge application, human task complementation, and multifunctional capabilities. By addressing the unique challenges of cybersecurity, these technologies enable organizations to safeguard their digital assets more effectively and efficiently.
This table presents various techniques and their corresponding algorithms in cybersecurity. Each approach provides a unique way to understand and counter threats in the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, from classification to clustering and using artificial intelligence with neuroscience.
| Technique | Description | Algorithms |
| Classification | Utilized to ascertain the credibility of a security event and its categorization within or outside a group. | Naive Bayes classifier, HMM, KNN, SVM, SOM, neural networks and decision trees |
| Pattern matching | Identifying harmful indicators and patterns within vast data sets. | Boyer Moore, KMP and entropy function |
| Regression | Analyzing trends in security occurrences and predicting machine and user behavior. | Linear regression, logistic regression and multivariate regression |
| Deep learning | Development of automated strategies for attack detection based on historical actions. | Deep Boltzmann Machine (DBM) and Deep Belief Networks (DBN) |
| Association rules | Issuing alerts upon recognition of similar attack patterns and assailants. | Apriori and Eclat |
| Clustering | Identification of anomalies and outliers, and grouping machines and users into clusters | . K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering |
| AI using neuroscience | Enhancing human intelligence through continuous learning, allowing for proactive threat detection, analysis, and insights. | Cognitive security |
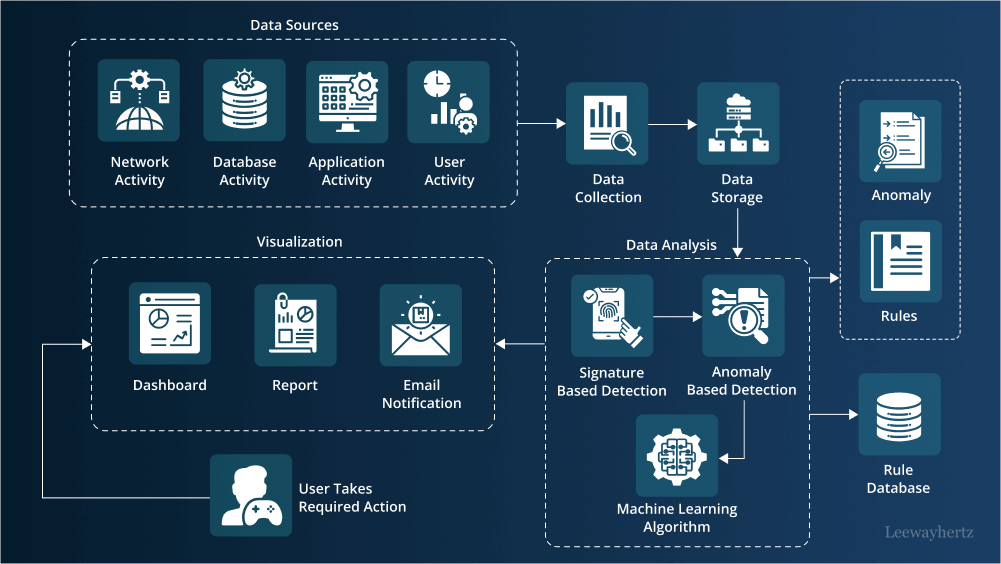
How is AI used in cybersecurity? A detailed breakdown of the process
The use of machine learning and deep learning in cybersecurity threat detection is carried out in a well-organized and structured manner. Thus, there is a clear and defined process or methodology in place for implementing ML and DL technologies to identify and respond to cybersecurity threats effectively. This systematic approach ensures that the use of these advanced technologies is coordinated, efficient, and able to provide reliable results in threat detection. First, security event data is captured from various enterprise sources as a foundation for training an attack detection model.
Once gathered, this data undergoes a meticulous preparation phase, including filtering and other adjustments, to make it suitable for model training. An appropriate ML algorithm is then selected and implemented on the prepared data to create an efficient attack detection model. The training time can vary between different algorithms.
After training, the model is rigorously tested with real-world enterprise data to ensure its ability to detect cyber attacks accurately. Filtered test data is processed by the attack detection model, which analyzes the information to identify potential threats based on patterns recognized during training. Factors such as the implemented algorithm influence the decision time or the time it takes for the model to determine if a specific data stream is an attack.
The results of this analysis are then made accessible to the user through a sophisticated visualization component, allowing a comprehensive view of the threat landscape. This systematic approach provides a robust defense against cyber threats, leveraging the power of ML and DL strategically and coherently.
How are enterprises leveraging AI in cybersecurity?
Enterprises increasingly turn to AI to enhance their cybersecurity efforts, particularly in incident response, threat detection, and automated remediation. Here’s how AI is being used:
1. Security Information And Event Management (SIEM) systems:
- SIEM systems leverage AI algorithms to analyze and categorize real-time security incidents. They achieve this by collecting and correlating data from diverse sources like network logs and intrusion detection systems. With machine learning, SIEM systems can quickly identify patterns that may indicate cyber threats, allowing security teams to respond promptly. For example, a financial institution might use AI-powered SIEM to detect and block potential Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, preventing service disruptions.
2. Threat intelligence platforms:
- AI-driven threat intelligence platforms sift through large amounts of data from internal and external sources, including social media feeds and dark web forums, to identify potential threats. Using NLP and machine learning, these platforms extract actionable insights to proactively identify emerging threats and vulnerabilities. For instance, an e-commerce company could use AI-powered threat intelligence to monitor social media for discussions related to its brand and alert its security team to any suspicious activity.
3. Automated remediation:
- AI enables automated remediation by triggering predefined actions based on the severity and classification of security incidents. This automation reduces the necessity for manual intervention and accelerates incident response times. For example, a healthcare organization might deploy AI-driven endpoint protection solutions to automatically isolate infected devices from the network upon detecting malware, preventing further spread and damage.
By incorporating AI into their cybersecurity strategies, enterprises can strengthen their defenses, respond more effectively to cyber attacks, and reduce the impact of potential attacks.
Benefits of AI in cybersecurity
There are many benefits to using AI in cybersecurity, and they can be grouped into various categories.
Increased efficiency
AI contributes to efficiency in cybersecurity by handling routine tasks, freeing up human analysts to focus on more complex issues. By quickly processing vast amounts of data, AI identifies patterns that may signify cyber threats, improving the efficiency of risk identification. Automation in tasks such as vulnerability scanning and patch management helps streamline these processes, reducing human effort. Furthermore, AI’s contribution to incident response processes and investigation accelerates identifying and remedying security breaches.
Improved accuracy
AI algorithms have the edge in detecting threats that might be difficult for humans, such as unknown malware or subtle patterns in network traffic. Its ability to analyze behavior allows AI to detect new malware variants, identifying malicious files even without known signatures. AI’s continuous learning and adaptability enhance the accuracy of cybersecurity defenses, allowing organizations to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Reducing costs
AI’s automation and improved accuracy play a role in cost savings. Automating routine tasks reduces human workload and associated costs. The accuracy in threat detection streamlines response processes, reducing false alarms and undetected breaches and avoiding unnecessary costs. The efficiency of incident response, proactive threat intelligence, and rapid response time minimize the impact and costs of a breach, such as financial losses and reputational damage.
Real-time threat detection and response
AI’s rapid data processing identifies suspicious patterns or anomalies in real time, enabling immediate threat detection and response. AI’s adaptability allows it to recognize emerging threats, providing proactive defense. Real-time alerts and automated response actions minimize the time between detection and response, reducing potential damage. This capability is vital in preventing data breaches and safeguarding organizational reputation.
Improved scalability
AI’s scalability enables effective analysis of massive data and efficient response to cyber threats, making it suitable for complex environments. AI can process extensive datasets from diverse sources like network logs and threat intelligence feeds. This scalability is essential in threat detection, identifying sophisticated attack techniques, and enabling coordinated responses across various endpoints. The synergy between AI’s scalability and human intelligence creates a robust defense against evolving cyber threats.
Integrating AI into cybersecurity has numerous advantages, from boosting efficiency and accuracy to minimizing costs, enhancing real-time responses, and providing scalability. These benefits make AI a valuable asset in today’s rapidly changing cybersecurity landscape, ensuring organizations are well-equipped to deal with modern and emerging threats.
Endnote
As we stand on the threshold of a new era in cybersecurity, the potential for transformation is clear. AI’s role in this field is evident and its future looks promising, with predictions pointing to continuous advancements. Although the technology is in its infancy, it shows signs of rapid growth, expanding its utility and application in security measures. The parallel evolution of AI with other emerging technologies like 5G and IoT opens new horizons for integrated and intelligent security systems.
Combining IoT’s vast data collection and AI’s insightful decision-making can forge a resilient shield against cyber threats. Furthermore, AI’s influence on the security industry and job market signifies a shift in roles, emphasizing collaboration between human intelligence and machine precision.
As organizations worldwide strive to enhance security at scale, they are met with a powerful ally in AI, capable of real-time detection, accuracy, and efficiency. However, it is vital to recognize that this technological leap requires informed adoption and a vigilant approach to risk management. The path to a secure digital future may be laden with challenges, but with AI’s progressive development, it is a path that seems increasingly navigable and full of potential.
Your organization’s security is too important to leave to chance, and LeewayHertz is your trusted partner in the fight against cyber threats. Leverage our AI-driven security solutions and fortify your defenses!
Listen to the article
Start a conversation by filling the form
All information will be kept confidential.
Insights
AI in accounting and auditing: Blazing new trails in financial management
AI has made significant inroads into the fields of accounting and auditing, redefining how financial data is processed, analyzed, and audited.
AI in telemedicine: Use cases, technologies, implementation and development
AI in telemedicine has a broad impact, encompassing improved diagnosis accuracy, remote monitoring, streamlined patient interactions, and enhanced care quality.
AI in trend analysis: Predicting the pulse of the market
In today’s fast-paced, data-driven world, deciphering patterns and trends is more crucial than ever, serving as a compass for organizations and individuals navigating the extensive seas of information.













