AI for workflow automation: Use cases, applications, benefits and development
Efficiency isn’t just a goal in today’s dynamic business environment; it’s a necessity. However, traditional workflow automation is no longer sufficient to meet the demands of this fast-paced world. The solution? Artificial Intelligence (AI). By seamlessly integrating AI technologies into workflow automation, businesses are unlocking a new domain of possibilities.
But what exactly does the future hold for workflow automation, and how can AI take it to the next level? Imagine a system that not only streamlines processes but also learns, adapts, and evolves over time. That’s the promise of AI-powered workflow automation. It’s not just about efficiency anymore; it’s about innovation and staying ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.
From data collection and integration to real-time analysis and decision-making, AI is reshaping the way workflows operate. Predictive and prescriptive analytics enable proactive decision-making, while continuous monitoring and optimization ensure that processes are always at their best.
This article explores the role of AI in workflow automation and its impact on businesses across various industries. By leveraging AI technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing, organizations can automate repetitive tasks, make data-driven decisions, and optimize their workflows like never before. We will also explore the future potential of AI-driven workflow automation in reshaping the business landscape.
- Understanding workflow automation
- How does AI enhance workflow automation?
- How does AI for workflow automation work?
- Applications of AI workflow automation systems across various industries
- How can GenAI enhance the automation of workflow processes and their subprocesses?
- How does workflow automation work?
- Steps to build an AI-powered workflow automation system
- How can LeewayHertz help in building AI-powered workflow automation solutions?
- LeewayHertz’s AI development services for workflow automation
- Challenges and considerations in implementing AI for workflow automation
- Future trends in AI-driven workflow automation
Understanding workflow automation
Workflow automation is the process of designing, executing, and automating a series of tasks, steps, or business processes using technology. This can involve automating simple, repetitive tasks or complex sequences of activities across different systems and departments. The primary goal is to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance productivity by minimizing the need for human intervention.
Workflow automation plays a pivotal role in streamlining processes, reducing manual errors, and increasing productivity. Traditionally, workflow automation relied on predefined rules and simple decision trees to execute repetitive tasks. However, with the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI), workflow automation has evolved to a whole new level.
Traditional workflow automation vs. AI-driven workflow automation
| Aspect | Traditional workflow automation | AI-driven workflow automation |
|---|---|---|
| Decision making | Rules-based decision-making, typically pre-programmed decision trees. | Utilizes AI algorithms for decision-making, allowing for more dynamic and adaptive decision processes. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, often rigid and predefined workflows. | Greater flexibility, can adapt to changing circumstances and learn from new data. |
| Adaptability | Limited adaptability, struggles with non-routine tasks or changing environments. | High adaptability, can handle non-routine tasks and adjust to changes in the environment. |
| Data processing | Primarily handles structured data. | Can process both structured and unstructured data, enabling deeper insights and analysis. |
| Predictive capabilities | Limited predictive capabilities rely on historical data and predefined rules. | Advanced predictive analytics can forecast outcomes based on real-time data and patterns. |
| Learning ability | No learning capability and operates based on pre-defined rules. | Can learn from historical data and user interactions, improving accuracy and efficiency over time. |
| Complexity handling | Limited capacity for complex tasks, may struggle with intricate processes. | Can handle complex tasks and processes, including those with multiple variables and decision points. |
| Human interaction | Minimal human-like interaction, typically limited to predefined responses. | Natural language processing and human-like interaction enable more intuitive and conversational interactions. |
| Cost | Initial investment can be lower, but may lack long-term efficiency. | Initial investment might be higher, but potential long-term savings through optimization and efficiency gains. |
| Time to deployment | Quick deployment, typically involves setting up predefined workflows. | Deployment might take longer due to training algorithms and data gathering but it offers more comprehensive solutions. |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic updates to adapt to changes in business processes. | Continuous learning and self-optimization, reducing the need for manual updates and maintenance. |
| Examples | ERP systems, basic automation tools. | Intelligent process automation, chatbots, cognitive automation. |
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
Benefits of implementing workflow automation
Implementing workflow automation offers numerous benefits for businesses of all sizes:
- Increased efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can significantly reduce the time and effort required to complete them, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Reduced errors: Manual processes are prone to errors. Workflow automation helps eliminate errors by ensuring consistency and accuracy in task execution.
- Cost savings: By reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency, workflow automation helps businesses save costs associated with labor, time, and resources.
- Faster decision-making: AI-driven workflow automation enables faster decision-making by analyzing data in real time and providing actionable insights.
- Improved customer experience: Streamlining workflows leads to faster response times, improved service delivery, and, ultimately, a better customer experience.
How does AI enhance workflow automation?
- Intelligent decision-making: AI workflow automation systems can make intelligent decisions based on data analysis and predictive modeling. By analyzing historical data and real-time information, AI algorithms can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and optimize workflow processes for maximum efficiency.
- Adaptive and self-learning: Unlike traditional workflow automation systems, AI-driven systems are adaptive and self-learning. Through continuous analysis of data and feedback, AI algorithms can adapt to changing conditions, learn from past experiences, and optimize workflow processes in real-time.
- Automation of complex tasks: AI enables the automation of complex tasks that were previously performed manually. By leveraging Machine Learning, NLP, and Computer Vision, workflow automation systems can automate tasks such as data entry, document processing, customer interactions, and decision-making, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing efficiency.
- Personalized and context-aware interactions: AI-driven workflow automation systems can personalize interactions based on individual preferences, historical behavior, and contextual information. By analyzing customer data and interactions, AI algorithms can deliver personalized recommendations, responses, and solutions, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Continuous optimization: AI enables continuous optimization of workflow processes by analyzing performance metrics, identifying bottlenecks, and suggesting improvements. Through real-time monitoring and analysis, AI-driven workflow automation systems can identify opportunities for optimization, reduce inefficiencies, and drive continuous improvement.
By leveraging the power of Artificial Intelligence, businesses can transform their workflow automation processes, drive efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape. AI-driven workflow automation not only improves operational efficiency but also enables businesses to deliver better customer experiences, drive innovation, and achieve their business objectives more effectively.
How does AI for workflow automation work?
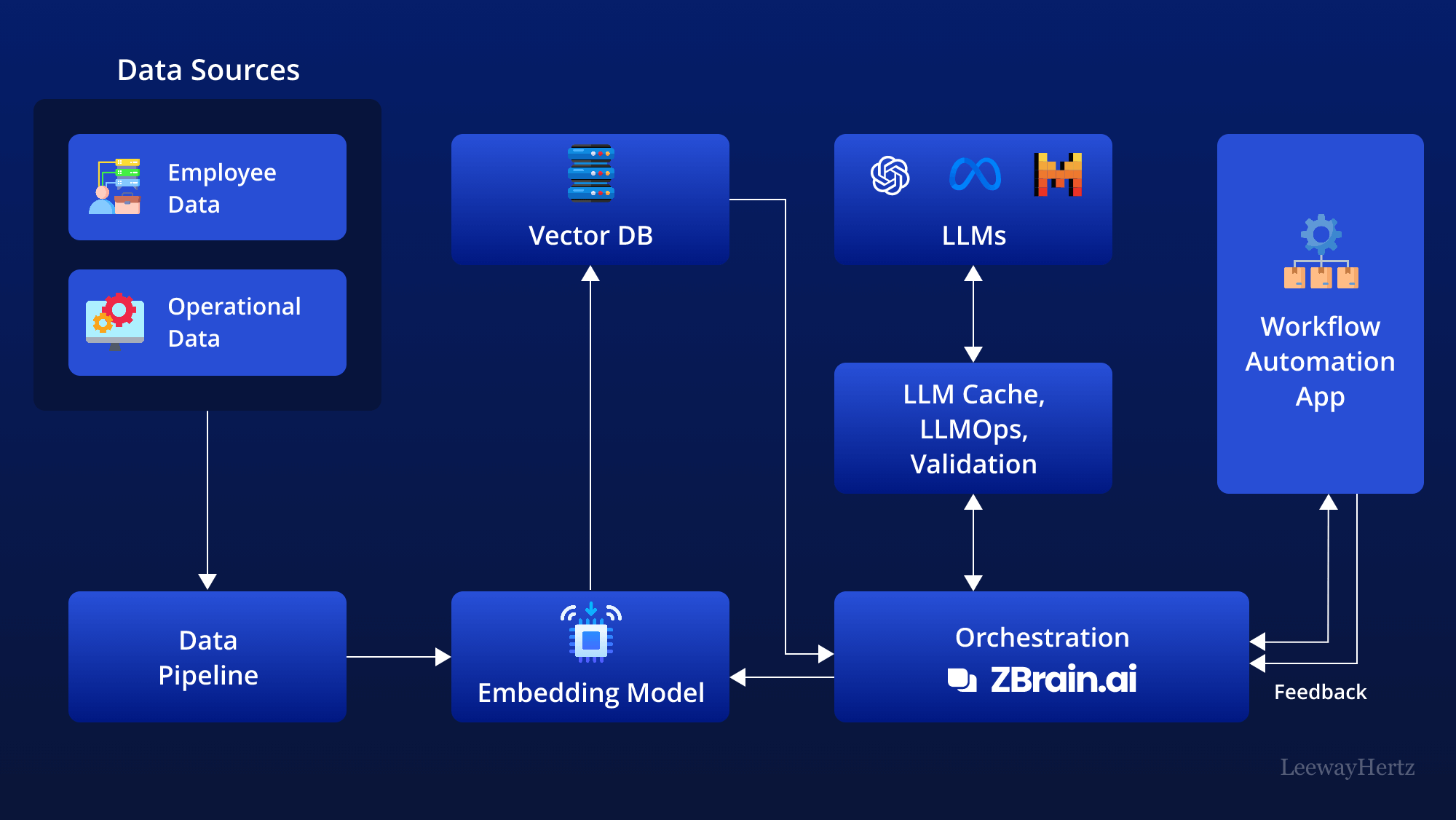
Incorporating AI into workflow automation processes involves various components to streamline task management, enhance productivity, and optimize resource allocation. It leverages powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) and integrates them with an organization’s proprietary data. This approach empowers businesses to automate repetitive tasks, streamline processes, and make data-driven decisions in real-time.
This AI-driven architecture leverages various components to streamline workflow automation. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Data sources: The process begins by gathering data from various sources relevant to workflow automation. This data can include:
- Task management systems: Information about tasks, deadlines, and resource allocation from task management platforms like Asana, Trello, or Jira.
- Employee data: Details about employee skills, availability, and performance metrics from HR databases and performance management systems.
- Customer data: Insights into customer interactions, preferences, and feedback from CRM systems and customer support platforms.
- Operational data: Data related to operational processes, equipment utilization, and supply chain logistics from ERP systems and manufacturing databases.
- Data pipelines: Data from the sources listed above are then routed through data pipelines. These pipelines are responsible for the ingestion, cleaning, and structuring of data, making it ready for further analysis.
- Embedding model: The prepared data is then processed by an embedding model. This model transforms the textual data into numerical representations called vectors that AI models can understand. Popular models include those from OpenAI, Google, and Cohere.
- Vector database: The generated vectors are stored in a vector database, which allows for efficient querying and retrieval. Examples of prominent vector databases include Pinecone, Weaviate, and PGvector.
- APIs and plugins: APIs and plugins like Serp, Zapier, and Wolfram play a key role by connecting different components and enabling additional functionalities, such as accessing extra data or performing specific tasks with ease.
- Orchestration layer: The orchestrating layer is critical in managing the workflow. ZBrain is an example of this layer that simplifies prompt chaining, manages interactions with external APIs by determining when API calls are required, retrieves contextual data from vector databases, and maintains memory across multiple LLM calls. Ultimately, this layer generates a prompt or series of prompts that are submitted to a language model for processing. The role of this layer is to orchestrate the flow of data and tasks, ensuring seamless coordination across all components within the architecture.
- Query execution: The data retrieval and generation process begins when the user submits a query to the workflow automation app. This query can be about anything relevant to task scheduling, resource allocation, or process optimization.
- LLM processing: Once received, the app transmits the query to the orchestration layer. This layer retrieves relevant data from the vector database and LLM cache and sends it to the appropriate LLM for processing. The choice of LLM depends on the nature of the query.
- Output: The LLM generates an output based on the query and the data it receives. This output can take various forms, such as task assignments, workflow optimizations, or resource reallocation recommendations.
- Workflow automation app: The validated output is then presented to the user through the workflow automation app. This is the core application where all the data, analysis, and insights converge. It presents the findings in a user-friendly format for managers and team members.
- Feedback loop: User feedback on the LLM’s output is another important aspect of this architecture. The feedback is used to improve the accuracy and relevance of the LLM output over time.
- Agent: AI agents step into this process to address complex problems, interact with the external environment, and enhance learning through post-deployment experiences. They achieve this by employing advanced reasoning/planning, strategic tool utilization, and leveraging memory, recursion, and self-reflection.
- LLM cache: Tools like Redis, SQLite, or GPTCache are used to cache frequently accessed information, speeding up the response time of the AI system.
- Logging/LLMOps: Throughout this process, LLM operations (LLMOps) tools like Weights & Biases, MLflow, Helicone, and Prompt Layer help log actions and monitor performance. This ensures the LLMs are functioning optimally and continuously improve through feedback loops.
- Validation: A validation layer is employed to validate the LLM’s output. This is done through tools like Guardrails, Rebuff, Guidance, and LMQL to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.
- LLM APIs and hosting: LLM APIs and hosting platforms are essential for executing workflow automation tasks and hosting the application. Depending on the requirements, developers can select from LLM APIs offered by companies such as OpenAI and Anthropic or opt for open-source models. Similarly, they can choose hosting platforms from cloud providers like AWS, GCP, Azure, and Coreweave or opt for opinionated clouds like Databricks, Mosaic, and Anyscale. The choice of LLM APIs and cloud hosting platforms depends on the project’s needs and developers’ preferences.
This structured flow provides a detailed overview of how AI facilitates workflow automation, leveraging various data sources and technological tools to streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and enhance productivity. Overall, AI automates various tasks involved in workflow management, improves efficiency, and enables a more agile and responsive organizational structure.
Applications of AI workflow automation systems across various industries
AI has numerous applications in workflow automation across various industries. Here are some examples:
Healthcare
- Document processing:
- Medical records management: AI can automate the extraction and classification of patient information from medical records, ensuring accurate data entry and easy access to patient history.
- Insurance claims processing: OCR and AI can process insurance claims forms, reducing manual labor and speeding up the claims approval process.
- Predictive analytics:
- Patient outcomes: AI can analyze patient data to predict potential health outcomes and recommend preventative measures.
- Resource allocation: Predictive analytics can forecast patient admission rates, helping hospitals optimize staffing and resource allocation.
- Quality control and assurance:
- Diagnostic imaging: AI-powered systems can analyze medical images to detect anomalies such as tumors or fractures, improving diagnostic accuracy.
Retail
- Customer service:
- Virtual shopping assistants: AI chatbots can assist customers in finding products, answering questions, and providing personalized shopping experiences.
- Customer feedback Analysis: NLP can analyze customer reviews and feedback to identify common issues and areas for improvement.
- Predictive analytics:
- Demand forecasting: AI can predict product demand, helping retailers manage inventory and reduce stockouts or overstock situations.
- Personalized recommendations:
- Product recommendations: AI analyzes customer behavior and preferences to suggest relevant products, enhancing the shopping experience and increasing sales.
Financial services
- Data entry and management:
- Automated data extraction: AI can extract and validate data from financial documents such as loan applications, reducing processing time and errors.
- Fraud detection: AI systems can analyze transaction patterns to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Predictive analytics:
- Credit scoring: AI can assess creditworthiness by analyzing historical financial data and predicting the likelihood of loan default.
- Risk management: Predictive models can identify potential risks in investment portfolios and suggest mitigation strategies.
- Customer service:
- Automated support: AI-driven chatbots can handle routine inquiries about account balances, transaction history, and financial products, freeing up human agents for more complex tasks.
Manufacturing
- Process optimization:
- Production line optimization: AI can monitor production lines in real-time, identifying inefficiencies and suggesting adjustments to improve throughput.
- Predictive maintenance: AI can predict equipment failures before they occur, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Quality control and assurance:
- Defect detection: AI-powered vision systems can inspect products for defects during the manufacturing process, ensuring high quality and reducing waste.
- Inventory optimization:AI can analyze supply chain data to predict inventory needs and optimize stock levels, reducing holding costs and preventing shortages.
Human resources
- HR and recruitment:
- Resume screening: AI can automatically screen resumes and rank candidates based on their fit for job requirements, speeding up the recruitment process.
- Candidate matching: AI can match job openings with the best candidates by analyzing skills, experience, and other relevant factors.
- Employee engagement:
- Sentiment analysis: AI can analyze employee feedback and engagement surveys to identify areas for improvement and enhance workplace satisfaction.
- Workforce planning:
- Talent management: Predictive analytics can forecast workforce needs and help HR managers plan for future hiring and training requirements.
Logistics
- Workflow orchestration:
- Route optimization: AI can optimize delivery routes based on traffic conditions, delivery windows, and other factors, ensuring timely deliveries.
- Task scheduling: AI can schedule and prioritize tasks for warehouse operations, improving efficiency and reducing delays.
- Supply chain management:
- Demand prediction: AI can forecast demand for products, helping logistics companies manage inventory and transportation resources effectively.
- Quality control:
- Shipment monitoring: AI can monitor the condition of shipments in transit (e.g., temperature, humidity) and ensure compliance with quality standards.
Real estate
- Property recommendation: AI can analyze customer preferences and historical data to recommend properties that match their requirements.
- Predictive analytics: AI can analyze real estate market trends to predict property prices and assess investment opportunities.
Legal
- Document analysis:
- Contract review: AI can analyze legal contracts to identify key clauses, obligations, and potential risks, speeding up the contract review process.
- Legal research: AI can analyze case law, statutes, and regulations to assist lawyers in legal research and case preparation.
- E-discovery: AI can analyze electronic documents to identify relevant information for legal proceedings, reducing the time and cost of e-discovery processes.
- Case prediction: AI can analyze historical case data to predict case outcomes and assist in legal strategy development.
Insurance
- Underwriting:
- Risk assessment: AI can analyze applicant data to assess risk and determine insurance premiums for policies such as life insurance, auto insurance, and property insurance.
- Fraud detection: AI can analyze claim data to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activity, helping insurance companies prevent and investigate fraudulent claims.
- Customer service:
- Claims processing: AI-powered chatbots can assist customers with filing insurance claims, checking claim status, and answering policy-related questions.
- Policy management: AI can automate policy issuance, renewal, and endorsement processes, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
How can GenAI enhance the automation of workflow processes and their subprocesses?
Generative AI offers transformative capabilities to enhance the automation of workflow processes and their subprocesses. By leveraging AI-driven models, organizations can streamline repetitive tasks, improve decision-making, and ensure higher operational efficiency. GenAI automates data analysis, communication, and process optimization, enabling businesses to scale their workflows with precision and adaptability.
Here’s a list of various sub-processes within workflows, categorized by major industries, showcasing how automation is applied in specific contexts across sectors:
1. Financial services and banking
GenAI streamlines complex financial processes, enhancing efficiency and customer experience across the banking ecosystem.
- Loan processing: Automates document review, credit analysis, and decision-making.
- Fraud detection: Analyzes transaction patterns and detects anomalies in real-time.
- KYC automation: Automates customer identity verification with intelligent data extraction.
- Compliance monitoring: Automates compliance checks and regulatory reporting.
- Risk management: GenAI models assess risks and recommend mitigation strategies.
- Payment processing: GenAI continuously learns and improves payment automation, optimizing workflows and accuracy.
- Investment portfolio management: GenAI dynamically rebalances portfolios based on market trends.
- Customer service and engagement: Personalizes advice, anticipates needs, and analyzes sentiment.
- Operations and back-office: Automates underwriting, streamlines compliance, and enhances fraud detection.
2. Healthcare
GenAI transforms healthcare operations by automating patient care, health records management, and compliance processes.
- Patient appointment scheduling: Automates appointment booking and reminders with personalized interactions.
- EHR management: Automates the organization and retrieval of patient records.
- Medical billing and coding: Streamlines billing processes with automated code suggestions.
- Prescription refill and orders: Automates prescription renewals and inventory management.
- Claims processing: Automates claim validation and approvals using intelligent document analysis.
- Compliance (HIPAA): GenAI helps healthcare organizations ensure data security and privacy compliance.
- Telemedicine: Automates patient tracking and care recommendations during telemedicine visits.
- Diagnosis and treatment planning: Analyzes images and data to aid in disease detection and treatments.
- Patient care and monitoring: Offers personalized advice, tracks medication adherence, and enables remote patient monitoring.
- Research and drug discovery: GenAI accelerates drug discovery and optimizes clinical trials.
- Administrative and operational tasks: GenAI streamlines the supply chain and automates staffing.
3. Manufacturing
GenAI optimizes production, quality control, and inventory management, driving efficiency in manufacturing workflows.
- Inventory management: Predicts stock levels and automates reordering.
- Production scheduling: Automates production schedules based on real-time demand.
- Quality control: Detects defects and automates quality monitoring.
- Equipment maintenance: Analyzes complex sensor data, predicting equipment failures and enabling proactive maintenance.
- Product lifecycle management: Streamlines design approvals and automates prototype feedback loops.
- Compliance audits: Automates safety and regulatory audits across facilities.
- Design and engineering: GenAI fuels design innovation by generating constraint-meeting starting points, letting engineers focus on refinement.
- Production optimization: Optimizes process parameters by analyzing real-time sensor data.
- Supply chain management: Enhances demand forecasting using historical and external data.
- Worker safety and training: Helps identifies safety hazards and customizes training programs for workers.
4. Retail and E-commerce
GenAI personalizes customer interactions and automates backend operations, transforming retail and e-commerce experiences.
- Order processing: Automates order validation and shipment scheduling.
- Inventory management: Predicts stock needs and automates reordering.
- Customer service: GenAI-powered chatbots resolve customer inquiries automatically.
- Marketing campaigns: Automates targeted customer campaigns based on behavior analytics.
- Loyalty programs: Automatically update rewards and send personalized offers.
- Product recommendations: GenAI personalizes cross-selling and upselling offers in real-time.
- Returns processing: Automates authorization and refund workflows.
- Customer experience enhancement: Enables product search through images and natural language search queries.
- Operations and logistics: Optimizes warehouse layouts and guides robotic picking.
- Fraud detection and prevention: Detects and prevents fraud by analyzing purchase patterns.
- Content and marketing personalization: Generates product descriptions and creates personalized email campaigns.
5. Insurance
GenAI enhances insurance workflows, from claims processing to fraud detection, improving operational accuracy and customer service.
- Claims processing: Automates document validation and claims adjudication.
- Policy underwriting: GenAI evaluates risks and automates policy issuance.
- Fraud detection: Detects fraud patterns through real-time data analysis.
- Customer onboarding: Automates onboarding with KYC and document submission.
- Renewal reminders: Sends automated reminders for policy renewals.
- Document management: Automates policy document retrieval and storage.
- Compliance: Ensures ongoing regulatory adherence automatically.
- Risk assessment and pricing: Creates personalized risk profiles using diverse data sources.
- Claims management and prevention: Estimates repair costs by analyzing damage from photos or videos.
- Customer service and engagement: Offers personalized policy recommendations based on customer data.
6. Education
GenAI automates administrative and learning processes, creating seamless and personalized experiences for students and educators.
- Student enrollment: GenAI streamlines admissions and registration tasks, enhancing efficiency and student experience while preserving ethical decision-making.
- Attendance tracking: Automatically logs student attendance data.
- Assignment grading: Automates grading and feedback using AI-based assessments.
- Course scheduling: GenAI optimizes course schedules and staff allocations.
- Learning management systems: Automates content delivery and tracks student progress.
- Financial aid processing: Streamlines the review and disbursement of financial aid.
- Alumni management: Automates engagement with alumni for events and donations.
- Personalized learning and support: Tailors learning materials to each student’s needs and progress.
- Content creation and curriculum development: Generates educational content like quiz questions and summaries efficiently.
- Administrative efficiency and insights: Optimizes resource allocation by analyzing enrollment and student needs.
7. Logistics and transportation
GenAI accelerates logistics and transportation efficiency by automating fleet management, shipment tracking, and order fulfillment.
- Fleet management: Automates vehicle maintenance schedules and route optimization.
- Shipment tracking: Monitors shipments and automates notifications in real-time.
- Order fulfillment: GenAI optimizes routing and automates proof of delivery.
- Inventory management: Predicts and automates restocking based on demand forecasts.
- Regulatory reporting: Automates the creation of compliance documents.
- Driver management: Schedules and tracks driver performance automatically.
- Demand sensing: Predicts shifts in demand using real-time data for proactive adjustments.
- Dynamic risk assessment: Updates shipment and supplier risk profiles in real-time.
- Smart contract execution: Automates smart contracts based on conditions in logistics.
- Proactive exception handling: Predicts delays, enabling early solutions.
- Personalized supply chain visibility: Provides real-time shipment tracking dashboards.
8. Human Resources (HR)
GenAI simplifies HR processes by automating recruitment, performance tracking, and payroll management, improving employee experiences.
- Recruitment: Automates candidate screening, interview scheduling, and onboarding.
- Performance management: Tracks performance metrics and automates feedback loops.
- Payroll: Automates key aspects of payroll processing, tax calculations, and benefits management.
- Training: Automates employee training and certification tracking.
- Time tracking: Automates timesheet approvals and attendance tracking.
- Leave management: Automates leave requests and balance updates.
- Skills gap analysis: Identifies skills gaps by analyzing job descriptions, trends, and internal data.
- Personalized learning: Creates tailored learning paths based on role, skills, and goals.
- Internal talent marketplace: Matches employees with relevant projects and mentorships based on skills.
- Employee sentiment analysis: Gauges sentiment from feedback to identify and address issues early.
- Personalized recognition: Suggests tailored rewards based on employee contributions and preferences.
- Predictive attrition modeling: Identifies employees at risk of leaving by analyzing performance and sentiment.
- Bias detection in hiring: Detects and mitigates bias in job descriptions and interview processes.
- DE&I (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) training personalization: Personalizes DE&I training based on employee demographics and roles
9. Legal
GenAI transforms legal operations by automating contract management, compliance, and case tracking, increasing productivity in legal workflows.
- Contract management: Automates contract generation and approval workflows.
- Litigation management: Automates case tracking and document handling.
- Compliance management: Monitors and automates adherence to legal regulations.
- IP portfolio management: Automates patent renewals and trademark tracking.
- Document automation: Automates the creation and processing of legal documents.
- Case management: Automates case scheduling and client updates.
- Legal research: Finds relevant case law and statutes.
- Contract review: Scans contracts for risks and inconsistencies.
- Litigation prediction: Forecasts case outcomes and costs.
- Legal chatbots: GenAI-powered chatbots offer basic legal guidance.
- Personalized legal services: Tailors legal documents and advice.
- Legal knowledge management: Organizes legal knowledge for easy access.
- Expertise finder: Identifies experts within law firms for collaboration.
10. Real estate
GenAI streamlines real estate operations by automating property management, lease renewals, and tenant communications for seamless management.
- Property management: Automates tenant communications and maintenance workflows.
- Lease management: Automates lease creation, renewals, and tenant updates.
- Tenant onboarding: Streamlines background checks and document processing.
- Facilities maintenance: Schedules and tracks repairs and maintenance requests.
- Property listings: Automates the posting and management of property listings.
- Compliance: Automates compliance with property regulations and audits.
- Property recommendations: Tailors property suggestions based on user preferences and budget.
- Property valuation: Provides accurate, automated property appraisals using market data.
- Targeted marketing: Creates personalized marketing campaigns by analyzing demographics and trends.
- Lead qualification: GenAI chatbots qualify leads, answer property-related questions and schedule viewings.
- Investment risk analysis: Assess real estate investment risks using market and property data.
GenAI serves as a powerful tool for automating workflow processes and their subprocesses, driving greater efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. GenAI integration streamlines tasks and unlocks deeper insights, driving innovation and better performance across industries.
How does workflow automation work?
Workflow automation employs task management software to route tasks and information between people and systems based on predefined rules and triggers. For example, when one system marks a task as complete, the automation can automatically send it to the next assignee and update dashboards. This process saves time over manual handoffs and minimizes errors.
Steps to start with workflow automation:
- Understand the current workflow:
- Gather information on how tasks flow among teams, focusing on project initiation, task completion criteria, scope of work, and bottlenecks.
- Determine what triggers each task to start and change.
- Outline the workflow visually:
- Create a visual draft of the workflow to identify inefficiencies and breakdown points.
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams to improve the draft and pinpoint wasteful practices.
- Identify integration needs:
- Determine tasks that require data integration from other systems and ensure the workflow software supports these requirements.
- Adjust the workflow as needed, such as splitting tasks into smaller subtasks to meet integration needs.
- Address workflow inefficiencies:
- Tackle issues like communication breakdowns and overdue tasks.
- Implement measures for task accountability and clarify the flow of information between systems.
- Build the workflow in automation software:
- Define each task and assign user roles within the software.
- Provide visibility through Gantt charts, process maps, calendars, etc., based on team needs.
- Create automated triggers and actions:
- Streamline recurring tasks with customized automation recipes or pre-built options.
- Continuously test and optimize:
- Resolve issues by testing and optimizing the automated workflow regularly.
- Establish performance metrics and key performance indicators to monitor efficiency and use dashboards to maintain high-level visibility into progress and blockers.
- Train the team:
- Conduct hands-on demonstrations to train the team in using the new automated workflow.
- Prepare teams for process changes and workflow optimizations with comprehensive change management plans.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
Steps to build an AI-powered workflow automation system
AI workflow automation combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies with workflow automation to streamline business processes, improve efficiency, and drive innovation. Here’s how AI-powered workflow automation works:
Data collection and integration
- Data sources: AI-powered workflow automation begins with the collection of data from various sources, including internal systems, databases, applications, sensors, and external sources such as websites, social media, and IoT devices.
- Data integration: The collected data is integrated and aggregated into a centralized data repository, such as a data warehouse or a data lake, where it can be accessed, processed, and analyzed by AI algorithms.
Data preprocessing and cleansing
- Data preprocessing: The raw data undergoes preprocessing to clean, transform, and normalize it, ensuring that it is consistent, accurate, and ready for analysis.
- Data cleansing: Data cleansing techniques such as deduplication, normalization, and outlier detection are applied to remove errors, inconsistencies, and redundant information from the data.
AI model training and development
- AI model selection: Based on the specific business objectives and use case, appropriate AI models and algorithms are selected, including Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision, and others.
- Feature engineering: Features or variables that are relevant to the business problem are selected, extracted, and engineered from the preprocessed data to train the AI models effectively.
- Model training: The AI models are trained using historical data to learn patterns, relationships, and trends, enabling them to make predictions, classifications, or decisions based on new, unseen data.
Workflow design and automation
- Process mapping: The workflow automation process is designed to map out the sequence of tasks, rules, decisions, and conditions that define the workflow.
- Task identification: Tasks that can be automated using AI are identified, such as data entry, document processing, decision-making, and customer interactions.
- Integration with AI models: AI models are integrated into the workflow automation system to automate decision-making, optimize processes, and improve efficiency.
Real-time data analysis and decision-making
- Real-time data processing: As new data is generated and received in real-time, it is processed, analyzed, and fed into the AI models for decision-making.
- Predictive analytics: AI algorithms use historical data and real-time information to make predictions, identify patterns, and anticipate future events, enabling proactive decision-making and optimization.
- Prescriptive analytics: AI algorithms provide recommendations and suggestions for optimal courses of action based on the analysis of data and business rules, helping to optimize workflow processes and improve outcomes.
Continuous monitoring and optimization
- Performance monitoring: The performance of the AI-powered workflow automation system is continuously monitored, measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as efficiency, accuracy, throughput, and customer satisfaction.
- Feedback loop: Feedback from users, stakeholders, and the AI system itself is used to identify areas for improvement, refine AI models, and optimize workflow processes over time.
- Continuous improvement: Through continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimization, the AI-powered workflow automation system evolves and improves, becoming more efficient, adaptive, and effective over time.
Human oversight and intervention
- Human-machine collaboration: While AI-powered workflow automation can automate many tasks, human oversight and intervention are still essential for complex decision-making, exception handling, and process optimization.
- User interface: User-friendly interfaces and dashboards are provided to enable users to monitor, manage, and interact with the AI-powered workflow automation system, providing input, feedback, and guidance as needed.
AI-powered workflow automation combines AI technologies with workflow automation to streamline business processes, improve efficiency, and drive innovation. By leveraging AI algorithms for data analysis, decision-making, and optimization, organizations can automate repetitive tasks, improve decision-making, and deliver better products and services to their customers.
How can LeewayHertz help in building AI-powered workflow automation solutions?
LeewayHertz is a leading software development company that specializes in building AI-powered workflow automation solutions. Leveraging our expertise in AI, ML, and Robotic Process Automation (RPA), we help businesses streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and drive innovation. Here’s how LeewayHertz can assist in building AI-powered workflow automation solutions:
- Custom AI solutions: LeewayHertz has a team of experienced AI engineers who can develop custom AI solutions tailored to the specific needs of your business. Whether you need intelligent document processing, predictive analytics, or conversational AI capabilities, LeewayHertz can build a solution that meets your requirements.
- End-to-end development: LeewayHertz provides end-to-end development services, from initial concept to final deployment and maintenance. We can help you identify automation opportunities, design an AI-powered workflow automation solution, develop the necessary software, and integrate it with your existing systems and processes.
- Expertise in AI technologies: LeewayHertz has deep expertise in a wide range of AI technologies, including natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, machine learning, and deep learning. We can leverage these technologies to build intelligent automation solutions that can analyze data, make predictions, and perform tasks autonomously.
- Integration with existing systems: LeewayHertz can seamlessly integrate AI-powered workflow automation solutions with your existing systems and processes, including ERP systems, CRM software, and other enterprise applications. This ensures that the automation solution works smoothly with your existing infrastructure and workflows.
- Scalability and flexibility: LeewayHertz builds AI-powered workflow automation solutions that are scalable and flexible, allowing you to adapt to changing business needs and scale your operations as required. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, LeewayHertz can build a solution that grows with your business.
- Security and compliance: LeewayHertz takes security and compliance seriously and ensures that all AI-powered workflow automation solutions adhere to industry best practices and regulatory requirements. They implement robust security measures to protect your data and ensure that your automation solution is safe and secure.
- Continuous support and maintenance: LeewayHertz provides ongoing support and maintenance for AI-powered workflow automation solutions, ensuring that your solution continues to perform optimally over time. They monitor the system, identify any issues, and provide timely updates and enhancements as needed.
Overall, LeewayHertz can help businesses harness the power of AI to automate their workflows, improve efficiency, and drive business growth. With their expertise in AI technologies and commitment to delivering high-quality solutions, LeewayHertz is the ideal partner for building AI-powered workflow automation solutions.
LeewayHertz’s AI development services for workflow automation
At LeewayHertz, we specialize in building AI-driven solutions tailored to the diverse needs of workflow automation across various industries. Our strategic AI/ML consulting empowers organizations to leverage AI for streamlined processes, improved productivity, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Our expertise in developing Proof of Concepts (PoCs) and Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) allows businesses to evaluate the potential impacts of AI tools in practical settings, ensuring that solutions are both effective and customized to specific operational requirements.
Our work in generative AI transforms routine tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and reporting, automating these processes to free up human resources for more strategic roles.
By fine-tuning large language models to the intricacies of industry-specific terminology and workflows, LeewayHertz enhances the accuracy and relevance of AI-driven communications and analyses.
Additionally, we ensure these AI systems integrate seamlessly with existing technological infrastructures, boosting operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities across various sectors.
Our AI solutions development expertise
AI solutions development for workflow automation typically involves creating systems that streamline operations, automate repetitive tasks, and enhance overall productivity. These solutions integrate key components such as data aggregation technologies, which compile and analyze information from diverse sources. This comprehensive data foundation supports predictive analytics capabilities, enabling proactive decision-making and efficient process management.
Machine learning algorithms are employed to tailor workflow automation strategies to specific operational needs, ensuring that each process is optimized for efficiency and effectiveness. These solutions often cover areas like process optimization, task automation, predictive maintenance, and resource management.
Overall, AI solutions in workflow automation aim to enhance operational outcomes, improve efficiency, and elevate the overall productivity of organizations.
AI agent/copilot development for workflow automation
LeewayHertz builds custom AI agents and copilots that enhance various workflow automation operations, enabling companies to save time and resources while facilitating faster decision-making. Here is how they help:
Task automation:
- Automating routine tasks such as data entry, report generation, and scheduling.
- Streamlining data validation and verification tasks to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Automating document processing, including scanning, categorization, and storage.
- Prioritizing tasks based on their urgency, complexity, and potential impact, ensuring the most critical tasks are addressed first.
- Dynamically assigning tasks to the most appropriate individuals or teams based on skills, workload, and availability, optimizing resource utilization.
- Identifying and handling exceptions or deviations from standard workflows, alerting human operators or triggering predefined actions to minimize disruption.
Advanced process optimization:
- Analyzing historical data to identify potential bottlenecks and predict their occurrence allows organizations to proactively adjust resources and avoid delays.
- Continuously monitoring workflow performance and adjusting processes in real-time based on data insights and feedback, ensuring optimal efficiency.
- Automatically identifying and analyzing existing processes, suggesting opportunities for automation and recommending optimal workflows.
Integration and scalability:
- Integrating with a wide range of existing software platforms, including CRM, ERP, and other business applications, enabling seamless workflow automation across different systems.
- Deploying on cloud platforms, allowing for scalable and flexible deployment, ensuring they can handle growing workloads and adapt to changes in business requirements.
Process optimization:
- Analyzing workflow data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Recommending process improvements based on real-time analytics and historical data.
- Implementing predictive maintenance to minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan.
Resource management:
- Optimizing resource allocation by analyzing usage patterns and predicting future needs.
- Automating inventory management to ensure timely replenishment and reduce wastage.
- Managing workforce scheduling to optimize productivity and reduce labor costs.
Customer service:
- Offering 24/7 virtual assistance to handle customer inquiries and support requests.
- Analyzing customer interactions to provide personalized responses and recommendations.
- Automating routine communication tasks such as appointment reminders and follow-ups.
- Analyzing customer sentiment during interactions and personalizing responses and recommendations to create a more empathetic and engaging experience.
- Analyzing incoming inquiries and automatically routing them to the most appropriate support agents based on expertise, availability, and the nature of the request.
Compliance and risk management:
- Automating compliance checks and ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Monitoring workflows for compliance with predefined rules and policies.
- Flagging potential compliance violations or discrepancies for further review.
AI agents/copilots not only increase the efficiency of operational processes but also significantly enhance the quality of customer service and strategic decision-making. By integrating these advanced AI solutions into their existing infrastructure, organizations can achieve a significant competitive advantage, navigating the complex operational landscape with innovative, efficient, and reliable AI-driven tools and strategies.
Challenges and considerations in implementing AI for workflow automation
While AI has the potential to transform workflow automation and drive significant business benefits, there are several challenges and considerations that organizations need to address when implementing AI-driven workflow automation solutions.
Data quality and availability
Challenge: AI algorithms require large volumes of high-quality data to learn effectively and make accurate predictions. Ensuring the availability of clean, relevant, and structured data can be a significant challenge for many organizations.
Consideration: Organizations need to invest in data quality management processes, data governance frameworks, and data integration solutions to ensure that the data used to train AI models is accurate, reliable, and representative of the real-world scenarios.
Integration with existing systems
Challenge: Integrating AI-driven workflow automation solutions with existing systems, databases, and legacy applications can be complex and time-consuming. Incompatibility issues, data silos, and disparate data formats can hinder the seamless integration of AI with existing infrastructure.
Consideration: Organizations need to develop a comprehensive integration strategy that addresses the interoperability challenges and ensures smooth data exchange between AI systems and existing applications. Application programming interfaces (APIs), middleware solutions, and data integration platforms can help facilitate seamless integration.
Scalability and performance
Challenge: As the volume of data and the complexity of business processes increase, AI-driven workflow automation solutions need to scale to meet the growing demands. Ensuring the scalability and performance of AI algorithms in large-scale production environments can be challenging.
Consideration: Organizations need to design AI systems with scalability and performance in mind, leveraging cloud computing resources, distributed computing frameworks, and scalable AI architectures. Continuous monitoring, performance tuning, and optimization are essential to ensure that AI systems can handle increasing workloads efficiently.
Ethical and regulatory considerations
Challenge: AI-driven workflow automation raises ethical and regulatory concerns related to data privacy, security, fairness, and transparency. Biases in AI algorithms, unintended consequences, and lack of interpretability can undermine trust in AI systems and lead to regulatory compliance issues.
Consideration: Organizations need to develop robust ethical guidelines, governance frameworks, and regulatory compliance mechanisms to ensure that AI-driven workflow automation solutions adhere to ethical standards, comply with regulatory requirements, and mitigate potential risks. Implementing transparency measures, bias detection algorithms, and ethical AI principles can help build trust and confidence in AI systems.
Change management and user adoption
Challenge: Introducing AI-driven workflow automation solutions can disrupt existing business processes and workflows, leading to resistance from employees and stakeholders. Lack of awareness, fear of job displacement, and uncertainty about the benefits of AI can hinder user adoption and acceptance.
Consideration: Organizations need to develop a comprehensive change management strategy that involves stakeholder engagement, communication, and training initiatives. Educating employees about the benefits of AI, involving them in the implementation process, and addressing their concerns and feedback are essential to fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and acceptance.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Challenge: Implementing AI-driven workflow automation solutions requires significant upfront investment in technology infrastructure, talent acquisition, and ongoing maintenance and support. Calculating the return on investment (ROI) and demonstrating the business value of AI initiatives can be challenging.
Consideration: Organizations need to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis and ROI assessment to evaluate the potential impact of AI-driven workflow automation solutions on key business metrics such as productivity, efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Developing a clear business case, setting realistic goals and expectations, and measuring the performance and impact of AI initiatives are essential to justify the investment and secure buy-in from senior management and stakeholders.
Security and privacy concerns
Challenge: AI-driven workflow automation solutions can introduce new security and privacy risks, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and misuse of sensitive information. Protecting confidential data, ensuring data privacy, and complying with data protection regulations are critical considerations for organizations.
Consideration: Organizations need to implement robust security measures, encryption techniques, access controls, and data anonymization methods to protect sensitive data and mitigate security risks. Conducting regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and compliance checks can help identify and address potential security issues proactively.
Successfully implementing AI-driven workflow automation solutions requires organizations to overcome various challenges and considerations related to data quality, integration, scalability, ethics, talent, change management, cost, security, and privacy. By addressing these challenges effectively and adopting a holistic approach to AI implementation, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI to drive innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage in today’s digital economy.
Future trends in AI-driven workflow automation
AI-driven workflow automation is rapidly evolving, and several future trends are shaping its development. Here are some key trends to watch out for:
- Hyper-automation: Hyper-automation is the concept of automating end-to-end processes across multiple systems and technologies. AI will play a crucial role in enabling hyper-automation by integrating various automation technologies, such as robotic process automation (RPA), intelligent business process management (iBPM), and machine learning (ML), to create seamless and intelligent workflows.
- Intelligent Process Automation (IPA): IPA combines traditional process automation with AI capabilities like natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and machine learning. IPA solutions can understand unstructured data, make decisions, and continuously learn and improve processes without extensive human intervention.
- Process mining and optimization: AI algorithms will be used to analyze process data and identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for optimization. Process mining techniques can uncover hidden patterns and insights, leading to more streamlined and efficient workflows.
- Adaptive and self-healing workflows: AI-driven workflows will become more adaptive and self-healing. Machine learning models can monitor workflow executions, detect anomalies or deviations, and automatically adjust or repair the workflows without human intervention.
- Predictive analytics and forecasting: AI models will be used to predict future workflow demands, resource requirements, and process outcomes based on historical data and real-time inputs. This predictive capability can help organizations proactively manage workloads, allocate resources, and mitigate risks.
- Low-code/No-code automation: Low-code and no-code platforms will become more sophisticated, enabling citizen developers and business users to create and automate workflows using AI-powered tools without extensive coding knowledge.
- Explainable AI: As AI-driven automation becomes more prevalent, there will be a growing demand for explainable AI (XAI) systems that can provide transparency and interpretability into the decision-making processes of AI models used in workflows.
- Ethical AI and governance: With increased automation and AI involvement in critical business processes, organizations will focus on developing and implementing ethical AI principles, governance frameworks, and responsible AI practices to ensure fairness, accountability, and transparency in automated workflows.
These trends highlight the growing integration of AI into workflow automation, enabling more intelligent, adaptive, and efficient processes across various industries and domains.
Endnote
The integration of AI into workflow automation is not just a trend; it is a transformative force reshaping the way businesses operate. As organizations strive for greater efficiency, agility, and competitiveness, AI-driven workflow automation emerges as a crucial tool for achieving these goals.
From streamlining repetitive tasks to enabling intelligent decision-making, the applications of AI in workflow automation are vast and far-reaching. By leveraging AI technologies, businesses can not only optimize their processes but also unlock new levels of productivity and innovation.
However, implementing AI-driven workflow automation comes with its challenges. It requires careful planning, consideration of ethical implications, and overcoming technical hurdles. Yet, with the right approach and guidance, businesses can successfully harness the power of AI to revolutionize their workflows.
Looking ahead, the future of AI-driven workflow automation holds even more promise. As AI technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see increasingly sophisticated solutions that further enhance efficiency, adaptability, and intelligence within organizations. Embracing these future trends will be essential for businesses looking to stay ahead in an ever-changing landscape.
Leverage the expertise of LeewayHertz’s AI consulting and development services to transform your workflows with AI-driven automation. Discover how our tailored solutions can enhance efficiency and drive innovation in your business processes.
Start a conversation by filling the form
All information will be kept confidential.

















