AI for invoice processing: Significance, use cases, benefits and implementation
For many businesses, invoice processing remains a tedious, time-consuming chore. Mountains o f paperwork clog inboxes, manual data entry drags on productivity, and the risk of errors lurks around every corner. A study reveals that 3.6% of manually processed invoices contain errors, exposing organizations to potential financial discrepancies and compliance challenges. But what if there was a way to automate this process, freeing up valuable resources and ensuring accuracy? Enter AI invoice processing, the technology transforming accounts payable (AP) departments.
Imagine a system that effortlessly captures invoice data from paper or digital formats with superhuman accuracy. Recent statistics illuminate the stark contrast between traditional methods and AI-driven solutions, revealing an extraordinary 99% accuracy in capturing invoice header data through automation. AI algorithms, trained on vast datasets, can decipher even the most complex layouts and formats, extracting key information like vendor names, amounts due, and purchase order numbers. Gone are the days of manual keying and human error; AI handles the heavy lifting, ensuring data integrity and streamlining the entire workflow.
Beyond data extraction, AI unlocks even greater possibilities. AI streamlines invoice processes by automatically routing them for approval based on pre-defined rules, flagging disparities against purchase orders before they impact your bottom line. Additionally, it automates tedious tasks, eliminates manual data entry errors, and even schedules payments according to pre-set parameters. Invoices are seamlessly captured, categorized, and validated, with data smoothly flowing into your accounting system. This newfound efficiency translates into faster payments for your vendors, improved cash flow, real-time financial insights and valuable time saved for your team.
But AI invoice processing isn’t just about speed. It also empowers you with deeper insights into your organization’s spending habits. By analyzing extracted data, you can identify trends, optimize procurement processes, and make data-driven decisions to improve your financial health.
Are you prepared to leave behind the burdensome paper trail and embrace a more efficient and streamlined approach to invoice management? Dive into this article to explore the transformative power of AI invoice processing and discover how it can change your accounts payable operations, leaving you with more time to focus on what truly matters – growing your business.
This article explores how AI transforms invoice processing by comparing traditional methods to AI-powered solutions, discussing AI’s crucial role in invoice processing workflows, providing implementation guidance, and highlighting the benefits of AI integration.
- The role of AI in invoice processing
- OCR-based vs. AI-based invoice processing
- How does AI in invoice processing work?
- Use cases of AI in invoice processing
- Streamlining invoice processing workflow with generative AI
- LeewayHertz’s AI development services for automated invoice processing
- How to implement AI in your invoice processing workflow?
- Benefits of AI-driven invoice processing
The role of AI in invoice processing
AI-based invoice processing leverages advanced technologies such as machine learning (ML), optical character recognition (OCR), natural language processing (NLP), and workflow automation to streamline the management of invoices. This system automates the extraction of data from invoices, validates the information, and processes it by routing the invoice through the necessary approval and payment channels. Here’s a breakdown of each component:
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms learn from historical invoice data to improve the accuracy of data extraction and processing over time.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): OCR technology scans and converts different types of invoices, whether printed or handwritten, into machine-readable text.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP interprets and understands the text data from invoices, allowing the system to accurately extract relevant information like vendor names, dates, and amounts.
- Workflow Automation: This automates the routing of invoices through the appropriate approval processes and payment systems, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing errors.
Together, these technologies enhance the efficiency and accuracy of invoice management, ensuring that invoices are processed swiftly and correctly.
OCR-based vs. AI-based invoice processing
Automating invoice processing can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy in financial operations. Below is a detailed comparison between OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and AI-based invoice processing solutions:
| Feature | OCR Invoice Processing | AI Invoice Processing |
| Technology | Optical Character Recognition (OCR) | Employs AI, machine learning, natural language processing, and deep learning. |
| Functionality | Converts scanned invoices into editable text. | Extracts, understands, and interprets data from invoices. |
| Data extraction | Limited to recognizing text, doesn’t understand context. | Recognizes text, identifies data fields (e.g., vendor, date, amount), validates data. |
| Accuracy | Highly accurate for well-formatted, consistent invoices. | More resilient to variations in format, handwriting, and quality. |
| Flexibility | Requires templates or rule-based configurations for different invoice formats. | Adapts to different formats automatically, handles dynamic layouts. |
| Error management | Requires manual intervention for errors and exceptions. | Minimizes manual interventions with smart error detection and correction. |
| Learning & improvement | Limited learning capability, primarily static. | Continuously learns from data, improving accuracy and adaptability over time. |
| Integration | Integrates with basic accounting systems. | Seamless integration with ERP and other accounting software. |
| Additional features | Limited to data extraction and conversion. | Can offer fraud detection, data validation, and deeper insights. |
| Costs | Usually lower initial cost , may require additional resources for manual effort. | Higher initial cost, but often brings greater ROI due to automation and efficiency gains. |
| Benefits | Improves data entry efficiency. | Streamlines entire invoice processing cycle, reduces costs, increases visibility and control. |
| Limitations | Struggles with complex formats, requires maintenance for new vendors, not self-learning. | Requires data security considerations, may require ongoing model training. |
| Suitability | Small-medium businesses with standardized invoices, basic data extraction needs. | Large enterprises with high invoice volume, complex layouts, and advanced data processing requirements. |
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
How does AI in invoice processing work?
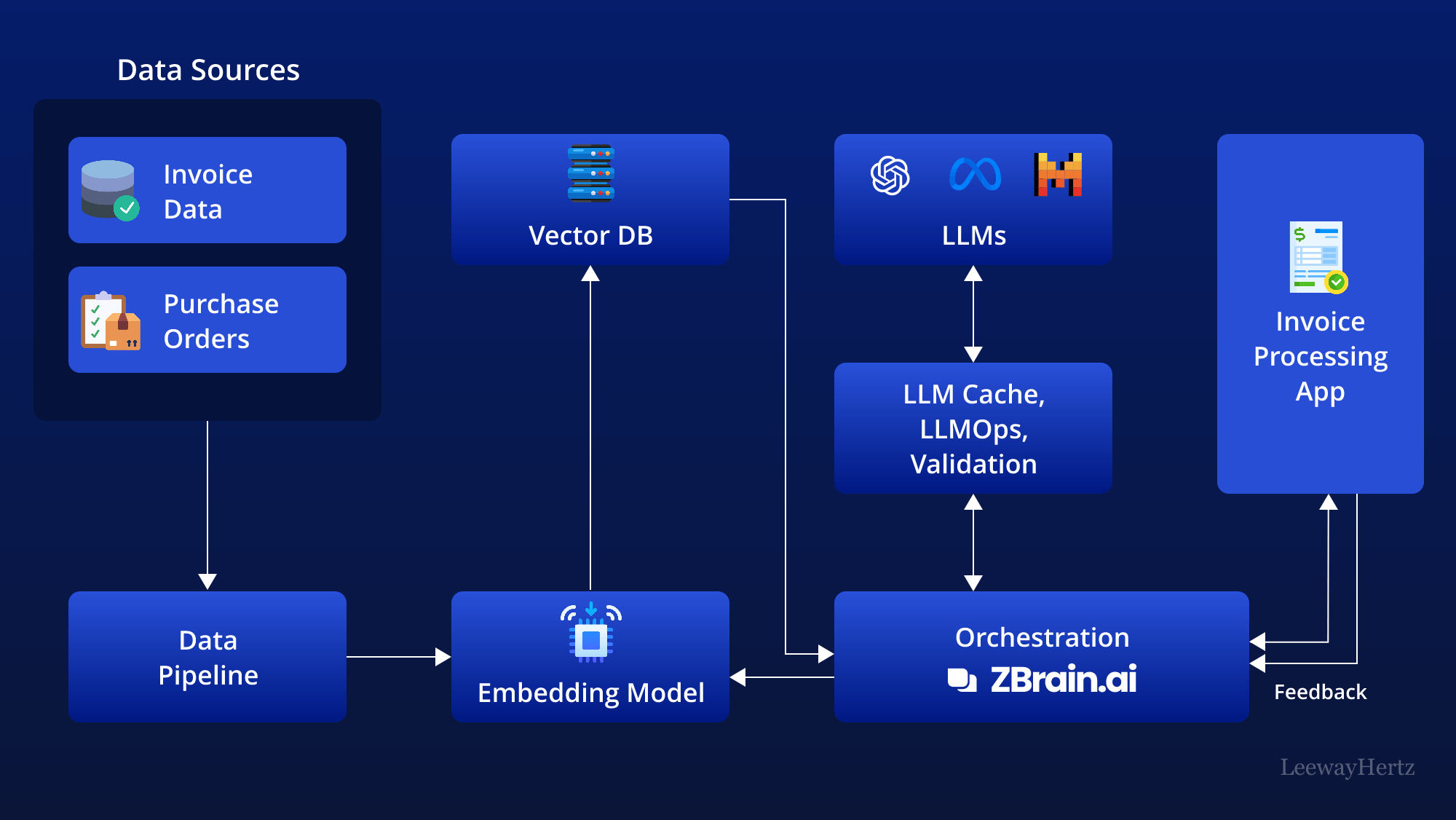
Incorporating AI into invoice processing involves various components to streamline data analysis, generate insights, and support decision-making. This approach goes beyond traditional invoice processing methods by leveraging powerful large language models (LLMs) and integrating them with an organization’s unique knowledge base. This technique generates valuable insights and enables businesses to make real-time data-driven decisions.
This architecture leverages various components to streamline the invoice processing task. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Data sources: The process begins by gathering data from various sources relevant to the invoice process. This data can include:
- Invoice data: The primary source contains details such as invoice number, date, vendor information, line items, quantities, prices, taxes, and total amounts.
- Purchase Orders (POs): Documents that provide information about the goods or services ordered, quantities, agreed prices, and delivery terms.
- Receipts and delivery notes: Proofs of receipt of goods or services used to match against invoices for verification.
- Vendor information: Data about suppliers, including contact details, payment terms, and transaction history.
- Payment records: Details of previous vendor payments, including payment dates, amounts, and methods.
- Data pipelines: Data from the above sources is then routed through data pipelines. These pipelines are responsible for ingesting, cleaning, structuring, and preparing the data for further analysis.
- Embedding model: The prepared data is then processed by an embedding model. This model transforms the textual data into numerical representations called vectors that AI models can understand. Popular models include those from OpenAI, Google, and Cohere.
- Vector database: The generated vectors are stored in a vector database, allowing efficient querying and retrieval. Examples of prominent vector databases include Pinecone, Weaviate, and PGvector.
- APIs and plugins: APIs and plugins like Serp, Zapier, and Wolfram play a key role by connecting different components and enabling additional functionalities, such as accessing extra data or performing specific tasks easily.
- Orchestration layer: The orchestrating layer is critical in managing the workflow. ZBrain is an example of this layer that simplifies prompt chaining, manages interactions with external APIs by determining when API calls are required, retrieves contextual data from vector databases, and maintains memory across multiple LLM calls. Ultimately, this layer generates a prompt or series of prompts submitted to a language model for processing. The role of this layer is to orchestrate the flow of data and tasks, ensuring seamless coordination across all components in this architecture.
- Query execution: The data retrieval and generation process begins when the user submits a query to the invoice processing system. This query can be about anything relevant to the invoices being processed, such as invoice details, payment status, discrepancies, or vendor information.
- LLM processing: Upon receipt, the invoice processing system forwards the query to the orchestration layer. This layer retrieves relevant data from the vector database and LLM cache and sends it to the appropriate LLM for processing. The selection of LLM depends on the specific characteristics of the query.
- Output: The LLM generates an output based on the query and the data it receives. This output can take various forms, such as summaries of factual information, identification of potential discrepancies, or generation of draft reports tailored to invoice processing needs.
- Invoice processing app: The validated output is then presented to the user through the invoice processing application. This central application is the core platform where all the data, analysis, and insights converge. It presents the findings in a user-friendly format tailored to users’ needs.
- Feedback loop: User feedback on the LLM’s output is another crucial aspect of this architecture. This feedback loop is instrumental in enhancing the accuracy and relevance of the LLM output over time.
- Agent: AI agents are pivotal in tackling complex challenges, engaging with the external environment, and refining their capabilities through post-deployment experiences. They accomplish this by employing advanced reasoning and planning techniques, utilizing strategic tools, and harnessing memory, recursion, and self-reflection.
- LLM cache: Tools like Redis, SQLite, or GPTCache are used to cache frequently accessed information, thereby accelerating the AI system’s response time.
- Logging/LLMOps: Throughout this process, LLM operations (LLMOps) tools like Weights & Biases, MLflow, Helicone, and Prompt Layer facilitate logging actions and monitoring performance. This ensures that the LLMs operate optimally and continuously improve through feedback loops.
- Validation: A validation layer is implemented to validate the LLM’s output. This involves utilizing tools such as Guardrails, Rebuff, Guidance, and LMQL to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.
- LLM APIs and hosting: LLM APIs and hosting platforms are crucial in executing invoice processing tasks and hosting the application. Depending on requirements, developers can choose LLM APIs like those offered by companies such as OpenAI and Anthropic or opt for open-source models. Similarly, they can select hosting platforms from cloud providers like AWS, GCP, Azure, and Coreweave or opt for opinionated clouds like Databricks, Mosaic, and Anyscale. The choice of LLM APIs and cloud hosting platforms depends on the project’s specific needs.
This structured flow offers a comprehensive overview of how AI streamlines invoice processing, harnessing diverse data sources and technological tools to generate precise and actionable insights. Through this process, AI automates numerous tasks involved in invoice processing, enhancing efficiency and enabling a more thorough analysis of financial transactions and vendor relationships.
Use cases of AI in invoice processing
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the manual handling of invoices poses significant challenges for organizations striving for efficiency and accuracy in their financial workflows. The incorporation of AI in invoice processing has emerged as a critical solution, overhauling the traditional accounts payable procedures and transforming the business landscape. Here is a detailed exploration of the pivotal role AI plays in streamlining and enhancing invoice processing:
- Automated data extraction: AI techniques, such as machine learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and pattern recognition, play a pivotal role in swiftly and accurately extracting relevant information from invoices. These techniques enable the system to analyze and interpret diverse invoice formats, languages, and writing styles, enhancing efficiency in the extraction process. By analyzing the text, AI systems can identify key data points such as invoice numbers, dates, vendor details, and line items, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors.
- Non-PO (Purchase Order) invoice processing: Traditional methods, such as OCR and rules-based programming, may struggle with non-standard invoices, such as handwritten ones. AI, particularly machine learning models, excels in handling diverse invoice formats and variations, accurately capturing nuanced information. It becomes adept at identifying and interpreting variations as it processes more invoices.
- Advanced analytics and insights: AI-driven analytics provide valuable insights into invoice data, enabling organizations to identify trends, optimize cash flow, and make informed financial decisions. By analyzing historical data and forecasting future expenses, AI helps organizations improve financial planning and forecasting accuracy.
- Customization and adaptability: AI solutions can be tailored to meet the specific needs and preferences of individual organizations. Whether it’s adapting to evolving cost categories or automating complex invoice workflows, AI offers flexibility and customization to optimize invoice processing according to organizational requirements.
- Document categorization: The combination of OCR, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and machine learning enables businesses to extract relevant data, understand contextual information, and categorize various documents sent along with invoices. This automation transforms documents into digital systems, enhancing search functionality.
- Three-way match process: AI tools, including Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and OCR bots, enhance the efficiency of the three-way match process. By automating tasks such as checking emails for invoices, reading invoice content, and comparing details with purchase orders, AI ensures accuracy and flags exceptions for further review.
- Automating repetitive tasks: Mundane and rule-based tasks, such as matching invoices to supplemental documents and invoice filing, can be efficiently automated using machine learning algorithms. AI streamlines these processes, freeing up valuable time for accounts payable teams.
- Compliance enhancement: AI contributes to compliance processes by automating tasks like sanctions screening. RPA, combined with NLP, streamlines the screening process, reduces manual errors, and ensures adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Fraud detection and error identification: AI’s pattern recognition capabilities are instrumental in identifying non-standard behavior in invoices and flagging potential fraudulent transactions. Additionally, AI algorithms help detect common errors, preventing issues like duplicate payments and data entry mistakes.
- Purchase order matching: AI algorithms can compare invoice data with corresponding purchase orders and delivery receipts to ensure consistency and accuracy. By automating the matching process, AI reduces the risk of errors and discrepancies, streamlining reconciliation efforts.
- Vendor performance analysis: AI can analyze invoice data to evaluate vendor performance based on metrics such as on-time delivery, pricing accuracy, and invoice resolution time. Insights derived from this analysis help procurement teams optimize vendor relationships and negotiate better terms.
- Multi-language support: AI-powered invoice processing systems can handle invoices in multiple languages, using natural language processing techniques to extract and interpret text accurately. This capability is essential for organizations operating in global markets.
- Automated payment scheduling: AI can schedule payments by analyzing invoice due dates and the company’s cash flow situation. It prioritizes payments to ensure critical invoices are paid on time while effectively managing cash reserves. This system helps avoid late fees and takes advantage of early payment discounts where applicable, optimizing overall financial management.
- Smart expense tracking: AI can track and categorize expenses from invoices by automatically recognizing and sorting costs into predefined categories. This provides detailed insights into spending patterns, enabling businesses to identify trends, manage budgets more effectively, and make informed financial decisions. Such tracking helps uncover potential areas for cost savings and improving financial planning.
- Invoice status tracking and alerts: AI can monitor the real-time status of invoices throughout their processing lifecycle, sending alerts for pending approvals, upcoming due dates, or discrepancies. This ensures that issues are addressed promptly. This proactive approach minimizes delays and errors, maintaining a smooth workflow and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- User-friendly dashboards: AI can enhance interactive dashboards, providing a comprehensive and real-time overview of key metrics for invoice processing.These dashboards display key information such as the number of invoices processed, pending approvals, and payment statuses. They provide actionable insights and enable finance teams to monitor performance, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions swiftly.
The integration of AI into invoice processing automates and streamlines workflows, guaranteeing accuracy and compliance while also unleashing advanced analytics to drive efficiency gains and deliver significant value to organizations navigating the dynamic landscape of financial operations.
Streamlining invoice processing workflow with generative AI
Invoice processing is a critical function for businesses, involving the receipt, verification, and approval of invoices before payment. Traditional invoice processing can be time-consuming and error-prone, particularly when dealing with high volumes and multiple suppliers. Generative AI offers significant advancements to streamline and automate the invoice processing workflow, reducing manual effort, improving accuracy, and accelerating payment cycles.
Key personas involved in the invoice processing workflow
- Accounts payable clerk: Uses GenAI to automate data entry and invoice matching, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
- Finance manager: Leverages GenAI for real-time financial insights and streamlined payment approvals.
- Vendor relations specialist: Utilizes GenAI to resolve discrepancies and manage vendor communications more effectively.
- Compliance officer: Employs GenAI for efficient regulatory monitoring, auditing, and record-keeping.
- IT administrator: Uses GenAI to maintain system performance and provide user support.
Here’s how generative AI enhances each stage of invoice processing workflow:
Invoice capture and validation
| Steps involved | Sub-steps | Role of generative AI |
| Receive invoices |
|
|
| Data extraction |
|
|
| Validation |
|
|
Approval and routing
| Steps involved | Sub-steps | Role of generative AI |
| Routing |
|
|
| Approval/rejection |
|
|
Payment processing
| Steps involved | Sub-steps | Role of generative AI |
| Data verification |
|
|
| Payment scheduling |
|
|
| Payment methods |
|
|
| Payment execution |
|
|
Invoice reconciliation
| Steps involved | Sub-steps | Role of generative AI |
| Data reconciliation |
|
|
| Reconciliation reporting | Generate reconciliation reports
Analyze reconciliation metrics Track outstanding issues Summarize trends and patterns |
|
| Exception handling |
|
|
Archive and reporting
| Steps involved | Sub-steps | Role of generative AI |
| Document storage and compliance |
|
Automates document storage with data classification and access controls.
Assists in categorizing and tagging documents automatically. Assists in regulating access based on user roles. Monitors and ensures compliance with regulations. Validates the accuracy of tax-related documents. |
| Auditing |
|
|
Integrating generative AI into invoice processing enhances efficiency, minimizes errors, and streamlines payment workflows. However, human oversight remains crucial for ensuring accuracy and making complex, judgment-based decisions.
LeewayHertz’s AI development services for automated invoice processing
At LeewayHertz, we develop customized AI solutions that streamline the complex and often tedious tasks associated with invoice processing. Our strategic AI/ML consulting empowers firms to utilize artificial intelligence for enhanced accuracy, faster processing times, and improved workflows.
Our expertise in developing Proof of Concepts (PoCs) and Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) allows firms to preview the potential impacts of AI tools in real scenarios, ensuring that the solutions are effective and tailored to the sector’s specific needs. We work with you to develop AI solutions that automate invoice data extraction, accelerate invoice matching and approval, identify and prevent fraud.
Our generative AI expertise helps transform routine tasks like report generation, document processing and data management, automating these processes to free up teams for more strategic roles.
By fine-tuning large language models to the specific nuances of financial terminology and vendor interactions, LeewayHertz enhances the accuracy and relevance of AI-driven communications and analyses. This fine-tuning improves the clarity and reliability of automated data extraction and financial reporting.
Additionally, we ensure that these AI systems integrate seamlessly with existing technological infrastructures. This integration enhances operational efficiency and decision-making in automated invoice processing systems, allowing for smoother transitions and continuous improvements in financial operations.
Our AI solutions development expertise
We focus on creating AI systems that transform traditional invoice processing methods. These systems include advanced OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to accurately capture and digitize data from various invoice formats, reducing human error and increasing processing speed. Our AI solutions are equipped with machine learning algorithms to identify discrepancies, such as duplicate invoices or incorrect data entries, ensuring that financial records are accurate and reliable.
Beyond data capture, our AI integrates with existing ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, allowing for seamless data flow and payment cycle automation, significantly reducing the processing time from receipt to payment. This integration ensures that all financial data is synchronized across platforms, providing real-time visibility into financial statuses and helping to manage cash flows more effectively.
Overall, AI solutions for automated invoice processing aim to optimize transaction processing outcomes, improve efficiency, and enhance the client experience.
AI agent/copilot development for automated invoice processing
LeewayHertz builds custom AI agents and copilots that enhance the invoice processing capabilities of businesses, allowing them to save significant time and resources while ensuring greater compliance and accuracy. Here is how they help:
- Data extraction and integration:
- Automatically capture and digitize invoice data accurately, reducing manual entry errors.
- Integrate extracted data with financial systems for streamlined processing and reconciliation.
- Categorize and file different types of invoices, streamlining the data management system.
- Compliance and error reduction:
- Automatically check and ensure all processed invoices comply with applicable financial regulations and internal compliance policies.
- Detect anomalies and inaccuracies in invoices, such as duplicate entries or incorrect figures, for immediate correction.
- Continually improve the accuracy and efficiency of the invoice processing workflow.
- Fraud detection and security:
- Monitor and analyze transaction patterns and flag activities that deviate from the norm as potential fraud.
- Protect sensitive invoice data against cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Maintain detailed logs of all invoice processing activities to support audits and provide transparency in financial transactions.
- Process optimization:
- Identify inefficiencies within the invoicing process, such as slow approval times or vendor response delays, and suggest improvements.
- Implement smart workflows that automatically route invoices based on predefined rules, reducing the time spent on manual oversight.
- Track and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of AI enhancements on the overall speed and quality of invoice processing.
- Cost management:
- Analyze historical spending data, helping to uncover patterns and manage costs more effectively.
- Project future expenses based on current spending trends and upcoming financial obligations.
- Recommend actionable strategies for cost savings by optimizing invoice processing and payment timing.
- Vendor relations and communication:
- Manage routine communications with vendors, such as sending acknowledgments and updating payment statuses, to improve vendor relationships.
- Track and report on vendor performance metrics to ensure compliance with service level agreements (SLAs).
- Automatically flag invoice discrepancies for human review and initiate communication with vendors to resolve issues promptly.
LeewayHertz’s AI solutions not only automate invoice processing tasks but also enhance firms’ financial and operational capabilities. By integrating advanced AI technologies, companies can handle high volumes of invoices with greater precision and efficiency, enabling them to optimize their financial operations and gain a competitive edge in the market.
How to implement AI in your invoice processing workflow?
Successfully implementing AI in your invoice processing workflow demands meticulous planning and strategic execution. Although each system has its nuances, adhering to these fundamental steps can significantly enhance your chances of success:
1. Deep dive into evaluation and analysis:
Process mapping: Create a visual representation of your current invoice processing workflow, noting each step from invoice receipt to payment clearance. Identify manual tasks such as data entry, approval routing, and reconciliation. Highlight bottlenecks where delays commonly occur, such as manual approvals or handoffs between departments. Also, pinpoint error-prone areas, such as manual data entry or misinterpreting invoice details.
Data analysis: Conduct a comprehensive analysis of your invoice data. Determine the volume of invoices received daily, weekly, and monthly to understand the workload. Categorize invoices based on their formats, whether they are structured (e.g., PDF, Excel), semi-structured (e.g., XML), or unstructured (e.g., scanned documents). Identify the essential data fields within invoices, including vendor information, invoice dates, line items, and totals, to understand the scope of data extraction required.
Feasibility assessment: Evaluate the potential benefits of integrating AI into your workflow. Assess whether tasks like data extraction, fraud detection, or compliance checks could be streamlined and improved with AI technologies. Consider factors such as the complexity of your invoice data, the frequency of errors, and the potential cost savings and efficiency gains from automation.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
2. Defining specific objectives and goals:
Accuracy: Set specific targets for improving accuracy in data extraction. Define measurable metrics, such as reducing the percentage of incorrect entries in key data fields by a certain percentage within a specified timeframe.
Speed: Establish goals for reducing processing time per invoice. Quantify the desired improvement in processing speed, whether it’s a percentage reduction in processing time or a specific number of days saved per invoice.
Compliance: Define the compliance requirements that the AI system should address. Specify automated checks for fraud detection, duplicate payment detection, and adherence to tax regulations to ensure regulatory compliance and risk mitigation.
3. Evaluating AI solutions:
Technical capabilities: Evaluate the technical features and capabilities of AI solutions, assessing the effectiveness of data extraction algorithms and the scalability of machine learning models to handle large volumes of invoices while maintaining accuracy in text extraction.
Integration options: Consider how AI solutions can be integrated seamlessly with your existing systems. Evaluate compatibility with accounting software, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and workflow management tools to ensure smooth data transfer and process integration.
Vendor reputation: Research the reputation and track record of AI solution providers. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and industry recognition to assess reliability, customer support, and the success of previous implementations.
4. Training your AI invoice processing system:
a. Data preparation:
- Data collection: Gather a diverse dataset of invoices that accurately represent the variability in your vendor base, formats, and layouts. Ensure the dataset includes a sufficient number of examples for each invoice format and data field.
- Data labeling: Consistently label relevant data fields across all invoices using labeling tools or services. Ensure accuracy and consistency in labeling to facilitate model training.
- Data cleaning: Standardize formatting, address missing values, and correct inconsistencies in the dataset to ensure high-quality training data and improve model performance.
b. Choosing your training method:
- Pre-built models: Consider using pre-built AI models for common invoice formats available through platforms like Microsoft AI Builder or Amazon Textract. These solutions offer out-of-the-box functionality and can be quickly deployed for standard use cases.
- Custom models: Opt for custom AI models using platforms like TensorFlow or PyTorch if you require more flexibility and customization to handle highly variable invoice formats or specific compliance requirements. Custom models may require more extensive training and fine-tuning but offer greater adaptability to your unique business needs.
c. Model training:
- Data splitting: Divide the labeled dataset into training, validation, and testing sets to train and evaluate the model’s performance. Allocate a sufficient portion of the dataset to each set to ensure accurate model assessment.
- Hyperparameter tuning: Fine-tune model parameters such as learning rate, batch size, and regularization techniques to optimize model performance. Experiment with different hyperparameter configurations to achieve the best results.
- Training: Train the AI model using your chosen platform or libraries, utilizing the labeled training data. Monitor training progress and performance metrics to assess model convergence and make adjustments as needed.
d. Evaluation and iteration:
- Testing: Evaluate the trained model’s performance on unseen data from the testing set to assess its accuracy and generalization capabilities. Measure performance metrics such as precision, recall, and F1 score to quantify model effectiveness.
- Error analysis: Analyze model predictions and identify patterns in prediction errors. Identify common error types and explore potential causes such as data quality issues or model limitations.
- Iterative improvement: Continuously iterate on the model training process based on feedback and evaluation results. Incorporate new labeled data, adjust model parameters, or explore alternative modeling approaches to improve performance incrementally over time.
5. Deployment and integration:
- Deployment options: Choose the deployment method that best fits your organization’s infrastructure and requirements. Consider cloud-based deployment options such as AWS/Azure or others for scalability and flexibility or on-premise deployment for data privacy and security concerns.
- API integration: Integrate the trained AI model with your existing systems and workflows using application programming interfaces (APIs). Develop custom integrations to enable seamless data exchange and automated invoice processing within your organization’s ecosystem.
6. Continuous monitoring:
- Establishing monitoring mechanisms: Set up robust monitoring systems to consistently track the performance of the AI invoice processing system post-deployment. Regularly analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) such as accuracy rates, processing times, and error rates to identify any deviations or anomalies promptly.
- Implementing alerts and notifications: Integrate alert and notification mechanisms within the system to automatically flag potential issues or discrepancies in the invoice processing workflow. This proactive approach enables swift intervention and resolution, minimizing the impact of any operational challenges.
- Regular review and model updates: Conduct periodic reviews of the AI model, adapting it to evolving business requirements, changes in invoice formats, or new regulatory guidelines. Regularly update the system to ensure its alignment with organizational objectives. Incorporate feedback from end-users and stakeholders to refine the model and enhance overall system effectiveness.
7. Ensuring employee engagement:
- Communication: Engage employees early in the AI invoice implementation process and communicate the benefits of automation and AI adoption. Address any concerns or misconceptions about job displacement and emphasize the collaborative nature of AI-driven workflows.
- Training: Provide comprehensive training and support to employees on using the new AI system effectively. Offer hands-on workshops, tutorials, and documentation to familiarize users with the system’s functionalities and workflows.
- Change management: Implement a change management strategy to facilitate the smooth adoption of the AI system. Encourage employee feedback and participation throughout the implementation process, and be responsive to concerns and suggestions for improvement. Foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation to ensure ongoing success and optimization of the AI-driven invoice processing workflow.
By following these steps and considering each aspect of implementation, you can integrate AI into your invoice processing workflow and reap the benefits of improved efficiency and accuracy.
Benefits of AI-driven invoice processing
AI-powered automated invoice processing transforms financial operations within organizations, offering a host of benefits. Here are a few:
- Swift invoice processing: Leveraging AI technology drastically reduces processing times compared to manual methods. For instance, manual data extraction could take over three and a half minutes per invoice, whereas AI-enabled extraction accomplishes the task in under 27 seconds. This swift processing expedites the entire workflow, ensuring timely vendor payments and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Precise data extraction: AI algorithms excel in extracting and validating data from invoices precisely, significantly minimizing errors inherent in manual data entry processes. Cognitive data capture, achieving up to 98% accuracy, enables users to process invoices with heightened precision and reliability, thereby minimizing discrepancies and ensuring the integrity of financial records.
- Enhanced workforce productivity: By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry and validation, AI liberates finance professionals from mundane activities, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives. This surge in productivity, enabling the processing of six times more documents simultaneously, optimizes resource allocation and drives organizational efficiency.
- Cost-efficiency: The efficiency gains from AI automation translate into tangible cost savings by slashing labor costs associated with manual invoice processing. Additionally, the reduction in errors leads to fewer financial discrepancies, bolstering the organization’s financial health and contributing to a more robust bottom line. Data from Aberdeen Group reveals that organizations leveraging AI can slash costs within their accounts payable departments by a substantial 30%.
- Optimized cash flow management: Swift invoice processing results in expedited approval and payment cycles, enhancing cash flow management. Organizations leveraging AI-powered automation capture nearly 75 percent of early payment discounts, fostering stronger relationships with suppliers and vendors while maximizing financial benefits.
- Fraud prevention and error detection: AI-powered systems can identify anomalies and patterns indicative of fraudulent invoices or errors, safeguarding organizations against financial losses and reputational damage.
- Regulatory compliance assurance: AI-driven solutions ensure strict adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies by systematically validating invoices against predefined rules and standards. This proactive approach mitigates the risk of non-compliance penalties and fosters a culture of regulatory integrity.
- Transparent financial processes: Automated invoice processing provides transparency throughout the invoice lifecycle, facilitating seamless tracking of financial transactions and simplifying audit processes. This transparency enhances accountability and ensures robust governance practices.
- Operational cost reduction: AI-powered automation drastically reduces operational costs associated with invoice processing, with companies experiencing up to 90% cost savings per processed invoice. Highly automated AP operations can save more than 85 percent in the average monthly cost to process 5,000 invoices, enabling organizations to allocate resources more efficiently and invest in strategic initiatives.
- Efficiency across financial operations: The efficiency gains from AI-powered invoice processing extend beyond invoice handling to optimize related financial processes such as accounts payable and financial reporting. This holistic optimization enhances overall financial operations and drives organizational agility. Moreover, Forrester’s findings underscore AI’s efficiency, indicating that it can expedite invoice approval processes by an impressive 80%.
- High-quality data insights: AI algorithms ensure consistent and accurate data collection from invoices, enhancing the quality of data available for analysis and reporting. This higher-quality data empowers organizations to make more informed decisions, driving strategic growth and competitiveness.
- Streamlined accounts payable workflow: AI-powered automation streamlines the entire accounts payable workflow, from invoice receipt to payment processing, resulting in smoother operations and heightened efficiency. This optimized workflow enhances collaboration, reduces bottlenecks, and ensures timely payments, thereby fostering stronger vendor relationships and driving organizational success.
Endnote
Integrating AI in invoice processing is not just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift. By automating tedious tasks, minimizing errors, and unlocking valuable insights, AI empowers businesses to streamline their financial operations and achieve greater efficiency. From faster processing times, streamlined workflows, and improved cash flow management to enhanced data accuracy and strategic decision-making, the undeniable benefits contribute to your business’s true financial transformation.
As AI technology continues to evolve, its invoice-processing capabilities will expand further. We can expect even more sophisticated solutions capable of handling complex invoices, adapting to diverse formats, seamlessly integrating with existing systems, and learning from historical data to identify anomalies and predict future trends. This will pave the way for fully autonomous invoice processing, freeing up valuable human resources for higher-level tasks and strategic initiatives.
While AI cannot completely replace human oversight, it is a potent tool to augment human capabilities. By embracing AI in invoice processing, businesses can unlock a future of optimized financial operations, improved profitability, and a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace. The future of invoice processing is intelligent, automated, and driven by AI – are you ready to be a part of it?
Enhance your invoice processing efficiency with advanced AI solutions! Engage LeewayHertz’s AI development services for seamless invoice processing automation, thereby streamlining your accounts payable processes.
Start a conversation by filling the form
All information will be kept confidential.
Insights
AI for enterprises: Redefining industry standards
AI for enterprises strategically deploys AI technologies and methodologies within large-scale organizations to enhance various operational aspects.
Machine learning for customer segmentation: Unlocking new dimensions in marketing
Customer segmentation is a powerful technique that helps businesses understand their customer base better and tailor their marketing strategies accordingly.
AI in healthcare: Use cases, applications, benefits, solution, AI agents and implementation
AI-powered predictive analytics identifies high-risk patients and prevents disease before it becomes severe. It can transform drug development processes for timely delivery and care.













