AI agents for retail and e-commerce: Capabilities, components, use cases, implementation, and benefits
The retail and e-commerce sectors, in particular, are witnessing a significant transformation through the adoption of AI agents. These intelligent systems are now indispensable assets for modern businesses, expected to push the autonomous AI market to a projected $28.5 billion by 2028. The global conversational AI market size is expected to grow to $13.9 billion by 2025. Moreover, 84% of e-commerce businesses are prioritizing AI solutions in their businesses. AI agents provide multiple solutions that improve efficiency, address specific pain points, and significantly enhance customer engagement.
AI agents are redefining interactions between retailers and customers by offering personalized product recommendations, managing inventory with predictive accuracy, and employing dynamic pricing strategies. These capabilities enable businesses to process vast amounts of data, identify consumer patterns, and generate insights that help anticipate market demands and optimize product offerings. This not only tailors the shopping experience to individual preferences but also drives operational decisions that can lead to substantial economic gains.
As online shopping continues to grow and consumers demand more integrated and seamless experiences across channels, AI agents are crucial in bridging the gap between digital convenience and physical retail services. Utilizing technologies like natural language processing and computer vision, these agents can interact with customers, guide them through complex buying processes, and support them post-purchase, including managing loyalty programs and handling returns.
This article delves into the expansive role of AI agents in the retail and e-commerce sectors, exploring their applications, benefits, and the emerging trends shaping this dynamic field. By understanding the capabilities and types of AI agents available, businesses can better harness these tools to thrive in an increasingly digital marketplace.
- Understanding AI agents
- Capabilities of AI agents in retail and e-commerce
- Types of AI agents used in retail and e-commerce
- How ZBrain’s generative AI agents are transforming enterprise operations
- Key components of AI agents for retail and e-commerce
- The e-commerce and retail industry’s challenges today
- Use cases and applications of AI agents in retail and e-commerce
- Key benefits of AI agents in retail and e-commerce
- Building LLM-based AI agents for retail and e-commerce: A step-by-step guide
- How can LeewayHertz help you build AI agents for retail and e-commerce?
- Looking ahead: Future directions for AI agents in retail and e-commerce
Understanding AI agents
An AI agent, often referred to as an intelligent agent, is a highly efficient virtual assistant designed to autonomously perform tasks by leveraging artificial intelligence. These agents are engineered to sense their environment, interpret data, make informed decisions, and execute actions to achieve specific goals. A defining feature of AI agents is their ability to adapt and enhance their capabilities over time. By utilizing advanced technologies such as Large Language Models (LLMs), AI agents continuously refine their skills through ongoing interactions, becoming increasingly sophisticated and effective.
Collaboration is crucial in autonomous AI systems. Multiple agents often work together, each assuming distinct roles like a specialized team. This cooperative strategy enhances problem-solving effectiveness, with each agent contributing its unique expertise towards a common objective, streamlining the approach to complex challenges.
What are LLM agents?
Although autonomous AI agents are designed for diverse purposes, this article focuses on those powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). At the core of an LLM agent is a large language model that enables robust dialogue and a variety of task performances. These agents harness the power of LLMs to process and understand language, perform tasks, reason, and exhibit a degree of autonomy. LLM agents represent an evolution of LLM capabilities, where they can be directed through prompts to perform actions, solve problems, and engage in nuanced conversations that extend beyond simple exchanges.
These agents are adept at understanding and generating human-like text, making their behavior appear intuitive and responsive. They can:
- Perceive: Sense or acknowledge the data from their environment.
- Remember: Recall past interactions or utilize provided information to enhance context understanding.
- Act: Carry out tasks based on processed information and insights.
- Utilize tools: Employ external tools to augment their capabilities and effectiveness.
- Apply logic: Use logical reasoning to produce coherent and contextually relevant outputs.
The capabilities of LLM agents
LLM agents are equipped with sophisticated AI technologies that enable them to function autonomously within digital environments. Their core capabilities include processing natural language, reasoning, and learning from interactions.
Natural language processing
- Understanding: LLM agents are adept at comprehending various forms of natural language inputs. This is essential for translation, summarization, and responding to queries, where they can interpret text and provide accurate responses.
- Communication: These agents can engage in dialogues, maintain context over time, and deliver coherent and relevant information to the conversation.
Chain of thought and reasoning
- Complex problem-solving: Employing a chain-of-thought approach, LLM agents can deconstruct complex issues into simpler elements for clearer reasoning and more effective decision-making.
- Graph of thought: They construct a graph linking different concepts and their relationships, enhancing their ability to solve problems.
Memory and learning
- In-context learning: LLM agents can learn from new information as it appears within the context of an ongoing interaction, thereby refining their responses without the need for retraining.
- Long-term memory and retrieval: Integrating a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline enables LLM agents to exhibit long-term memory capabilities, recalling and utilizing past interactions to inform current decisions.
The role of LLM-powered agents in retail and e-commerce
LLM agents transform vast amounts of unstructured text data into actionable insights and enable the execution of complex tasks that were previously challenging with simpler models. Their role in the e-commerce and retail sector highlights these capabilities:
- Natural Language Understanding and Generation: They can interpret user queries and respond in a way that mimics human conversation.
- Sophisticated pattern recognition: This technique identifies trends and patterns within large datasets, which is crucial for predicting consumer behavior and optimizing inventory management.
- Contextualized decision-making: Make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the current context, enhancing customer interactions and personalization.
These capabilities are vital for enhancing the retail experience. For example, an LLM agent can interact with customers, providing personalized shopping advice based on past purchases and browsing behaviors. Furthermore, they can manage complex customer service inquiries, automate routine tasks, and even drive marketing strategies by analyzing consumer data to predict trends.
| What can AI agents do? | Considerations for using AI agents |
|---|---|
| Close the gap in qualified staff | Might require human oversight in some situations |
| Tackle narrowly scoped tasks | Best suited for specific, well-defined tasks |
| Perform specific tasks well, repeatedly, with zero attrition | Setup requires technical skills and development |
| Increase overall automation rate | May need human intervention for complex decision-making |
| Reduce costs | Complement existing strategies to enhance customer experience |
| Reduce tier 1 and repetitive tasks for human agents | Training and integration into existing systems may be required. |
| Enhance tier 2 support by assisting human agents | Occasionally may generate inaccurate responses. (need for monitoring) |
The integration of LLM agents in retail and e-commerce streamlines operations and creates a more engaging and personalized shopping experience. As these technologies continue to evolve, their impact on the retail landscape is expected to grow, reshaping how businesses interact with their customers and manage their operations.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
Capabilities of AI agents in retail and e-commerce
AI agents are transforming retail and e-commerce by enhancing data management, optimizing operational processes, and improving decision-making and customer interactions. These intelligent systems streamline mundane tasks and play crucial roles in strategic planning and customer interactions.
Autonomy
AI agents can operate independently, which is crucial for automating routine tasks such as reordering and adjusting pricing based on real-time market data. This capability ensures operations continue smoothly without constant human intervention, allowing businesses to react quickly to market changes.
Data collection and analysis
AI agents excel in gathering, cleansing, and integrating data from multiple sources, such as ERP and CRM systems, social media platforms, and customer feedback. They act as advanced analytical tools, providing forecasts and strategic insights crucial for informed decision-making.
Process automation and optimization
AI agents automate and optimize routine tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and return orders handling. They manage exceptions and errors and continuously learn from anomalies to enhance efficiency. For instance, task-oriented agents adjust prices in real-time based on demand, competition, and other external factors.
Collaboration
AI agents enhance collaboration across various departments—from warehouse staff and marketing teams to customer service representatives—ensuring that processes are aligned and informed. This capability is vital for maintaining seamless operations from inventory management to customer service.
Adaptability
AI agents can learn from interactions, which is essential for personalizing shopping experiences and efficiently managing stock levels. They adapt their responses and strategies based on consumer behavior and feedback, continuously improving their effectiveness.
Decision-making and execution
AI agents assist with critical decisions regarding stock levels, logistics, marketing strategies, and customer engagement, ensuring these decisions are based on robust, data-driven insights. They also execute decisions that enhance the customer experience, such as offering personalized discounts.
Mobility
With the ability to navigate different digital environments, AI agents are instrumental in gathering and utilizing consumer behavior data across various platforms. This mobility allows them to track customer interactions and preferences seamlessly across different touchpoints, enhancing the ability to offer personalized experiences.
By leveraging these capabilities, AI agents drive increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer experiences, helping retail and e-commerce businesses thrive in a competitive market landscape. Their integration into various aspects of operations leads to significant growth and enhanced competitiveness.
Types of AI agents used in retail and e-commerce
While this article primarily focuses on LLM-powered AI agents, such as conversational and task-oriented agents, it’s important to briefly cover the broader spectrum of AI agent types and their relevance to the retail and e-commerce sectors.
Conversational agents
Conversational agents use advanced natural language processing technologies to simulate engaging human conversations. In retail and e-commerce, these agents are pivotal for enhancing customer service by handling inquiries such as product details, stock availability, and order status with high efficiency and personalization. They understand context and nuances, enabling them to generate responses that mimic human interaction, thus improving the customer shopping experience.
Task-oriented agents
Task-oriented agents are designed to achieve precise goals, focusing on efficiency and effectiveness in executing predefined tasks. In the retail sector, these AI agents are adept at tasks like automating check-out processes, managing inventory, and optimizing logistics workflows, contributing significantly to operational efficiency.
Reactive agents
These are the simplest forms of AI agents, operating based on the current state of their environment without retaining any memory of past interactions. For example, in e-commerce, reactive agents can quickly adjust pricing based on competitor pricing or manage stock levels in response to real-time sales data.
Deliberative agents
Equipped with symbolic reasoning models, these agents engage in planning and negotiation to achieve their goals. In retail, they are crucial for supply chain management, where strategic planning and coordination with other agents (suppliers, logistics providers) are essential.
Hybrid agents
Combining the strengths of reactive and deliberative approaches, hybrid agents offer robustness and adaptability alongside strategic planning capabilities. This makes them particularly effective in managing customer relations and inventory across various channels in retail.
Model-based agents
Model-based agents operate using an internal model to understand and predict their environment, which is particularly useful in partially observable environments. In e-commerce, these agents could predict customer behavior or optimize supply chain operations by maintaining and adjusting their state based on real-time data inputs.
Goal-oriented agents
These agents are programmed to achieve specific objectives, evaluating the potential consequences of their actions to make the best decisions that align with their goals. In retail, a goal-oriented agent might manage a promotional campaign to maximize engagement and sales while adhering to budget constraints.
Utility-based agents
Utility-based agents operate in complex decision-making environments, evaluating different states based on a utility function to optimize outcomes like profit or customer satisfaction. In e-commerce, these agents might manage dynamic pricing strategies to maximize revenue based on consumer demand and market conditions.
Information agents
These agents manage, manipulate, or collate information from multiple distributed sources. In e-commerce, they enhance market intelligence by aggregating consumer data and insights, facilitating more informed decision-making.
Interactive agents
Designed to engage with users, these agents interpret human input and provide responsive outputs, enhancing customer service and user experience. In retail, interactive agents could assist customers in navigating online stores and providing product recommendations based on user preferences and previous interactions.
Learning agents
Possibly the most advanced, these agents improve their performance over time based on experience. In e-commerce, learning agents adapt their strategies for customer interaction, inventory management, and marketing based on the outcomes of their previous actions and changing market trends.
Knowledge-based agents
Knowledge-based agents utilize a repository of structured information and rules to make informed decisions and provide expert advice. In retail, these agents could analyze customer data and market trends to offer personalized shopping experiences or optimize marketing strategies.
Cognitive agents
These agents are equipped with advanced decision-making capabilities, utilizing machine learning to analyze and interpret complex datasets. They are ideal for roles requiring analytical depth, such as predicting market trends or analyzing customer behavior patterns for strategic planning.
By integrating various AI agents, retail and e-commerce businesses can harness a blend of adaptability, efficiency, and intelligence crucial for leveraging technology to stay competitive in the digital era. As these agents continue to evolve, their potential to transform industry practices grows, making them fundamental to the future of AI-driven business operations.
How ZBrain’s generative AI agents are transforming enterprise operations
ZBrain AI agents bring cutting-edge generative AI capabilities to the retail and e-commerce landscape, enhancing operations with intelligent automation, personalized experiences, and actionable insights. By utilizing large language models (LLMs) and integrating seamlessly into retail ecosystems, these agents enable businesses to achieve creative, customer-centric, and operational excellence.
ZBrain AI agents: Key features and benefits:
1. Seamless system integration
ZBrain AI agents integrate effortlessly with retail and e-commerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, or custom solutions, ensuring smooth alignment with existing workflows and tools.
2. Continuous improvement through feedback
Human feedback loops empower these agents to constantly refine their outputs, improving personalization, customer engagement, and operational accuracy over time.
3. Proprietary data integration
The agents incorporate your unique customer and inventory data, enabling tailored recommendations, and better inventory management that aligns with your business needs.
4. Low-code workflow customization
Through Flow, businesses can create tailored, multi-step workflows to automate key retail processes, such as order processing, customer segmentation, and personalized marketing campaigns.
5. End-to-end customer journey automation
From personalized product recommendations to automated order fulfillment, ZBrain AI agents manage the entire customer journey, ensuring seamless operations and enhanced customer satisfaction.
6. Cloud and model agnostic
These agents are designed to operate across any cloud platform—AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, or private infrastructure—making them scalable and versatile for retail and e-commerce environments.
By harnessing the power of ZBrain AI agents, retail and e-commerce businesses can deliver exceptional customer experiences, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
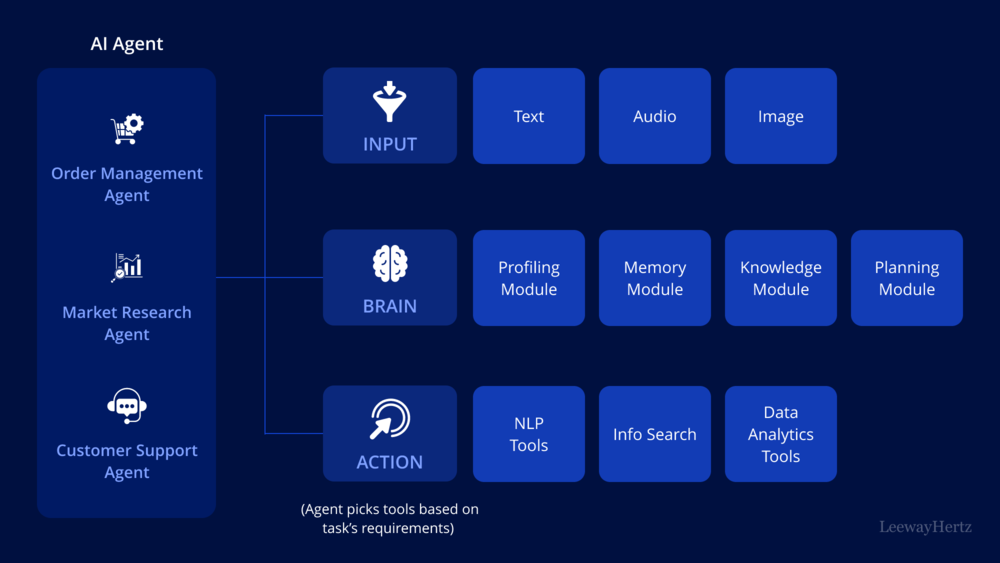
Key components of AI agents for retail and e-commerce
The architecture of AI retail and e-commerce agents comprises several crucial components, facilitating the processing of input data, reasoning, action planning, and execution based on contextual requirements.
Input: This component captures and processes diverse inputs from users and other agents, predominantly in auditory, textual, and visual formats. These inputs guide the agent’s actions and decisions.
Brain: Essential for cognitive functions, including reasoning, planning, and decision-making, the brain integrates several modules: profiling, memory, knowledge and planning. The profiling module defines the agent’s role and function, establishing its purpose for a given task. The memory module stores past interactions, enabling the agent to learn from prior experiences. The knowledge module houses domain-specific information aiding in planning and action. Finally, the planning module determines appropriate actions based on specific task requirements.
Action: This component executes planned actions, leveraging the brain’s processes. An LLM-based AI retail and e-commerce agent can decompose complex tasks into manageable steps, each associated with specific tools from its toolkit. This ensures efficient and accurate task execution by utilizing the right tools at times.
The e-commerce and retail industry’s challenges today
The retail and e-commerce sectors are undergoing rapid transformations driven by technological advances and shifts in consumer behavior. These changes bring numerous challenges that businesses must address to stay competitive and meet evolving consumer expectations. Here’s an overview of the pressing issues facing the industry today:
Fleeting consumer loyalty
With no barriers to switching brands and the ease of comparing options online, consumer loyalty is increasingly fleeting. Retailers must constantly innovate and improve customer experiences to retain consumers, a challenge compounded by the expectations set by industry giants like Amazon. The growth of online shopping has lowered barriers to entry, resulting in a crowded marketplace. The dominance of platforms like Amazon and Alibaba sets high expectations for variety, availability, pricing, and delivery, challenging other retailers to meet these standards with significant resource investment, particularly in logistics and customer service. This intense competition pressures margins and demands continuous innovation and differentiation.
Contextual personalization
Consumers expect highly personalized experiences tailored to their preferences and behaviors. Achieving contextual personalization requires advanced data analytics and the integration of insights across all customer touchpoints, presenting challenges in data management and application. This issue is compounded by the high standards set by industry giants like Amazon, which leverages features like “Customers also bought” to provide highly personalized shopping experiences. These recommendations, tailored to individual shopping behaviors, raise consumer expectations and set a benchmark for personalization that other retailers must meet or exceed to maintain customer loyalty and prevent churn.
Data security and privacy
As data collection increases to enhance user experiences, so does the responsibility to protect it. With the increasing amount of data being collected to enhance customer experiences, retailers face the dual challenge of protecting sensitive information against breaches and complying with stringent data protection regulations. Consumers are more aware and concerned about how their data is used and protected.
Siloed analytics
Many retailers struggle with siloed data systems that hinder the holistic analysis of customer data. This fragmentation makes obtaining a comprehensive view of customer behaviors and preferences difficult, complicating efforts to optimize or personalize experiences across various channels.
Technological integration
While technology offers solutions, integrating new technologies poses challenges, particularly for established retailers with legacy systems. The costs of upgrades and staff training are substantial, alongside the challenges of selecting suitable technological solutions.
Labor shortages and dissatisfaction
The retail sector often faces labor shortages and low employee satisfaction, which leads to increased attrition, higher training costs, and staffing issues. These issues not only impact customer experience but also increase operational burdens.
Differentiation in a saturated market
The sheer availability of options for consumers makes differentiation increasingly challenging. Retailers must find unique ways to stand out in a market where customers can find nearly anything, anywhere.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
Use cases and applications of AI agents in retail and e-commerce
AI agents are transforming retail and e-commerce by automating processes, enhancing customer experiences, and driving data-driven decisions. From personalized recommendations to inventory optimization, these agents empower businesses to streamline operations and stay competitive in dynamic markets. Lets explore the use cases of AI agent in retail and e-commerce and how ZBrain helps:
Market research and analysis
| Use case | Description | How ZBrain helps |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer sentiment analysis | Analyze customer reviews, social media, and feedback to gauge customer sentiment about products or brands, identifying trends and potential areas for improvement. | ZBrain can aggregate data from multiple sources and provide actionable insights to help businesses refine strategies. |
| Competitive analysis | Track competitor pricing, promotions, and product offerings to provide insights into market positioning and identify gaps or opportunities for differentiation. | ZBrain’s competitor news aggregation agent can automate competitor’s news classification and summarize relevant information, providing teams with timely insights for informed decision-making and proactive strategy adjustments. |
| Market segmentation | Segment customer bases into distinct groups based on demographics, preferences, and behavior, allowing for more personalized marketing efforts. | ZBrain can segment customers effectively, supporting targeted campaigns and product recommendations. |
Personalized shopping experiences
| Use case | Description | How ZBrain helps |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized product recommendations | Analyze customer behavior, purchase history, and preferences to suggest tailored products. | ZBrain uses customer data to deliver real-time, personalized suggestions, enhancing shopping experiences and increasing conversions. |
| Dynamic content customization | Adjust website or social media content based on customer preferences, such as banners or layouts. | ZBrain’s social media content generator agent automates creating platform-specific posts aligned with brand guidelines. It ensures consistent messaging across LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter, saving time and effort for marketing teams. |
| Virtual shopping assistants | Act as personal shopping guides, assisting customers in finding products and answering queries during their shopping journey. | ZBrain can provide conversational support, helping customers navigate the store and make informed decisions effortlessly. |
| Tailored promotions | Offers customized discounts or deals based on customer demographics, preferences, and shopping behavior. | ZBrain designs and delivers personalized promotional campaigns, increasing customer engagement and loyalty. |
| Cross-sell and upsell strategies | Suggest complementary or higher-value products based on customer selections and browsing history. | ZBrain can identify relevant cross-sell and upsell opportunities, boosting revenue while meeting customer needs. |
| Location-based personalization | Provide tailored recommendations or offers based on customers’ geographic locations. | ZBrain uses geolocation data to recommend nearby store deals or location-specific products, improving the shopping experience. |
| Personalized pricing | Offer individualized pricing based on customer behavior, preferences, or loyalty status, ensuring customers receive targeted pricing incentives. | ZBrain can analyze customer profiles and purchasing history to tailor dynamic pricing offers that increase conversion and customer retention. |
Order management and substitution
| Use case | Description | How ZBrain helps |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative suggestions | Recommend the best alternatives when specific items are unavailable, ensuring customer satisfaction and maintaining sales momentum. | ZBrain uses real-time inventory data and customer preferences to suggest suitable substitutes, reducing lost sales and improving experiences. |
| Real-time order updates | Provide customers with real-time updates on the status of their orders, reducing the need for customer service inquiries. | ZBrain’s order status update agent can deliver accurate, timely order updates, improving transparency and trust. |
| Returns and refunds processing | Handle the entire returns process, validating requests, initiating refunds, and updating inventory records, reducing manual effort and errors. | ZBrain’s refund validation agent can automate return and refund workflows, ensuring faster processing and seamless customer experiences. |
| Enhanced product search | Use natural language processing to understand customer queries and deliver accurate, relevant search results. | ZBrain can interpret customer queries, even complex or conversational ones, and provide precise product recommendations, simplifying the shopping experience. |
Automated customer interaction and issue resolution
| Use case | Description | How ZBrain helps |
|---|---|---|
| Automated ticket creation | Automatically create support tickets based on customer inquiries, issues, or requests, capturing relevant details without manual input. | ZBrain ticket creation agent can automatically extract key information from customer queries and generate detailed support tickets, ensuring accurate tracking. This automation reduces response times, enhances efficiency, and ensures timely resolution. |
| Ticket categorization | Categorize support tickets by type, urgency, and other factors, ensuring they are routed to the appropriate department or team for faster resolution. | The ticket categorization agent analyzes and categorizes incoming support tickets by issue type, streamlining the process and improving response times by accurately routing tickets to the appropriate team. |
| Ticket prioritization | Analyze ticket content and automatically prioritize tickets based on the severity or urgency of the issue, ensuring high-priority cases are addressed first. | ZBrain assesses the context of each ticket to assign priority levels, ensuring critical issues are handled promptly and efficiently. |
| Escalation management | Identify tickets that require escalation and automatically route them to senior staff or specialized teams, ensuring swift action on complex issues. | ZBrain monitors ticket progress and triggers escalations for unresolved or high-priority tickets, ensuring the right experts handle them. |
| Ticket closure | Automate personalized closure notifications for resolved support tickets, ensuring clear and consistent customer communication. | ZBrain’s ticket closure notification agent can generate tailored notifications that reflect the resolution of a support ticket, enhancing communication consistency and improving customer satisfaction. |
Supply chain optimization
| Use case | Description | How ZBrain helps |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory management | Monitor inventory levels in real-time, triggering reorders or reallocations when stock levels fall below thresholds to prevent stockouts or excess inventory. | ZBrain can track inventory across multiple channels, automatically updating stock levels and triggering timely reordering. |
| Warehouse optimization | Optimize warehouse operations by managing stock placement, routing, and order picking, increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs. | ZBrain can suggest optimal warehouse layouts and logistics strategies based on demand patterns, improving speed and accuracy in fulfillment. This ensures efficient stock placement, faster order picking, and reduced operational costs. |
| Supplier relationship management | Evaluate supplier performance by analyzing delivery times, quality, and costs, helping retailers maintain strong and reliable supplier relationships. | ZBrain analyzes supplier data to assess performance and recommend improvements or changes to supplier contracts. |
| Logistics and route optimization | Optimize delivery routes and shipping schedules, reducing transportation costs and ensuring timely deliveries. | ZBrain can use data to suggest the most efficient delivery routes, minimizing delays and cutting transportation expenses. |
| Product lifecycle management | Track the lifecycle of products from production to sale, ensuring timely restocking, identifying obsolete items, and managing product end-of-life strategies. | ZBrain monitors product lifecycle data to recommend timely restocking, discontinuation, or promotion strategies. |
| Dynamic reorder point optimization | Adjust reorder points based on analyzed data, such as sales velocity, stockouts, and lead times, to improve inventory replenishment accuracy. | ZBrain calculates optimal reorder points based on changing demand signals and supply chain conditions, reducing stockouts. |
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
Key benefits of AI agents in retail and e-commerce
Let’s detail the benefits and business impact of leveraging LLM-powered agents, emphasizing their unique capabilities and how they contribute to enhancing business operations and customer experience.
Enhanced user experience
LLM-powered agents excel in processing and understanding natural language, enabling them to engage customers in meaningful conversations. These interactions are more natural and capable of understanding nuances, humor, and intent, greatly enhancing the user experience.
Enhanced operational efficiency
AI agents automate both customer-facing and operational tasks, such as handling inquiries and managing inventory data, which traditionally consume significant human resources. By automating these processes, LLM agents free up human staff to focus on more strategic and complex tasks, boosting overall productivity and operational efficiency.
Personalized and contextual service
With their advanced capabilities, LLM agents deliver personalized recommendations and advice by analyzing individual customer data such as past purchases, browsing behavior, and preferences. This level of personalization not only improves customer satisfaction but also increases loyalty and conversion rates.
Multilingual support
Communicating in diverse languages enables LLM agents to support a broad customer base, breaking language barriers that often hinder global commerce. This capability expands market reach and ensures a consistent customer service experience worldwide.
Reduction in operational costs
By automating routine customer interactions and back-office tasks, AI agents reduce the need for extensive human customer support teams. This automation significantly saves labor costs and allows teams to focus on more complex and high-value interactions.
Enhanced data processing and analytics
LLM agents process and analyze vast amounts of customer data from various interactions. This capability allows for sophisticated trend analysis and market insight generation, enabling retailers to make informed decisions about product placements, marketing strategies, and inventory management.
Quick deployment and easy integration
Modern LLM agents are designed to be integrated and deployed quickly, often within a few weeks, minimizing the lead time and technical challenges associated with new technology adoption.
Reduced Average Handling Time (AHT)
By automating the resolution of common inquiries and transactions, AI agents significantly reduce the average handling time, boosting efficiency and enabling human agents to address more complex issues.
Improved agent assistance
LLM-powered agents support human agents by providing quick access to information, suggested responses, and action steps. This support not only improves human agents’ accuracy but also reduces their cognitive load during interactions.
Improved Agent Experience (AX)
AI agents offload the burden of repetitive and routine customer inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex and rewarding interactions. This shift enhances job satisfaction among customer service staff and improves their efficiency and effectiveness in handling unique or challenging issues, thereby enhancing the overall agent experience.
Quick deployment and scalability
AI agents can be deployed swiftly, often within weeks, allowing businesses to enhance their operations quickly. Further, they are highly scalable, effortlessly handling increased interactions during peak shopping periods without compromising performance or customer experience. This ensures that businesses can adapt to market demands and customer needs swiftly and efficiently.
Deliver knowledge efficiently
Leveraging generative AI and vector search capabilities, AI agents provide immediate, accurate responses across various channels. This technology empowers agents to deliver pertinent information swiftly, ensuring that customers receive knowledgeable assistance without delays and enhancing the customer service experience.
Improved accessibility and availability
Providing 24/7 support on any channel, AI agents ensure that help is always available, improving accessibility for customers and ensuring they can receive assistance whenever needed.
Reduced errors and improved decision-making
The precision of LLM agents minimizes the risk of errors common in manual processes, such as inventory mismanagement or customer data mishandling. Their ability to analyze large datasets with high accuracy also supports better decision-making, reducing costly business mistakes.
Building LLM-based AI agents for retail and e-commerce: A step-by-step guide
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming the retail and e-commerce sectors by automating complex processes and enhancing customer experiences. With LLM-powered AI agents, businesses can personalize shopping, optimize inventory management, and improve customer interactions. This section provides a detailed walkthrough of building your own LLM-powered AI agent specifically designed for retail and e-commerce applications.
Define the business objectives
- Scope definition: Clearly outline the specific retail tasks or challenges you wish your AI agent to tackle, such as customer service automation, personalization of shopping experiences, or inventory management. Clearly outline the specific retail or e-commerce domain you want to target (e.g., fashion, electronics, groceries) and the key challenges you want the AI agent to address.
- Task-oriented approach: Identify the precise functionalities your AI agent should perform:
- Customer interaction: Automate and personalize customer interactions to improve engagement and satisfaction.
- Inventory analysis: Manage and analyze stock levels to optimize supply chain operations.
- Sales optimization: Enhance sales strategies through personalized promotions and recommendations.
- Price optimization: Adjusting prices based on market demand and competitor analysis.
- Product recommendations: Suggesting relevant items based on customer preferences and behavior.
Select the right LLM platform
Select a base LLM that aligns with your retail/e-commerce needs. Here are some powerful options:
- OpenAI’s GPT family (GPT-3.5, GPT-4): Renowned for their impressive text generation, summarization, translation, and creative writing capabilities. GPT-4 is excellent for natural language understanding and generation making it ideal for customer interactions. Access is typically through an API.
- Google’s PaLM 2 (Pathway Language Model 2): This model boasts strong performance in reasoning, coding, and multilingual tasks. It is highly beneficial for global e-commerce platforms. Access is usually via Google’s AI platform or specific services like Vertex AI.
- Meta’s LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI): LLaMA is available in different sizes, making it adaptable to various e-commerce tasks. This model is adaptable to various retail tasks, from product descriptions to market analysis. Access is often granted through research partnerships or specific releases.
- BLOOM: A powerful open-source LLM ideal for multilingual tasks.
- Hugging Face Transformers: This isn’t a single LLM but rather a library (and a community) that provides access to a vast collection of pre-trained LLMs, including many mentioned above. This platform makes experimenting with and comparing different LLMs for your retail tasks easier.
- Factors to consider:
- Model size: Larger models are generally more capable but require more computational resources.
- Performance: Evaluate the model’s accuracy and efficiency on tasks similar to your needs.
- Licensing: Based on your budget and usage requirements, consider open-source options (e.g., BERT) or commercial APIs (e.g., OpenAI’s GPT-3 API).
Data collection and preparation
Quality data is crucial: Gather relevant, high-quality datasets specific to your retail/e-commerce domain. This might include:
- E-commerce data:
- Customer data: Purchase history, browsing behavior, demographics, and feedback.
- Product data: Descriptions, reviews, images, product catalogs, and inventory levels.
- Sales data: Transaction history, price changes, and promotions.
- Store data (if applicable): Customer interactions, store inventory, sales figures, and customer feedback.
- Market data: Competitive pricing, trends, industry reports and consumer preferences.
- Data cleaning and preprocessing: Ensure the data is clean, organized, and formatted correctly to train the LLM effectively.
- Data cleaning: Remove irrelevant information, correct errors, and handle missing data.
- Data formatting: Ensure consistent structure and formatting (e.g., using JSON, CSV) to make it compatible with the LLM.
Train the LLM (for the specific retail/e-commerce domain)
- Domain adaptation: Fine-tune the pre-trained LLM on your specific retail and e-commerce data to enhance its understanding of your business domain and customer base.
- Prompt engineering: Experiment with different ways of phrasing prompts to elicit the most accurate and relevant responses for retail scenarios. For example, providing context about the customer’s preferences or past purchases can improve the quality of product recommendations.
Develop the AI agent architecture: Building the brain and body
- Modular design: Design the AI agent as a system with distinct modules, each responsible for a specific function:
- Input processing: Handles user queries and commands.
- LLM interaction: Interacts with the trained LLM to generate responses and insights.
- Output generation: Presents the LLM’s output in a user-friendly format, potentially using natural language generation (NLG) to create conversational responses.
- Memory and context: This enables the agent to remember past interactions and maintain context during multi-turn conversations.
Implement Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
- Query interpretation: Develop NLU modules to accurately interpret customer queries and commands. For example, identify the intent behind a customer’s question (e.g., product search, order tracking, customer support).
- Intent recognition: Train the agent to understand the user’s intent (e.g., finding specific information, searching specific products, comparing different options).
- Entity extraction: Train the agent to identify and extract key entities from text, such as product names, brands, sizes, and colors. This information can be used to provide targeted recommendations.
Integrate knowledge bases and external systems
- Knowledge is power: Integrate external knowledge bases and databases to provide the AI agent with a wider range of information to draw upon.
- Product catalog: Use product catalog to access real-time product information, inventory levels, and pricing.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Integrate with your CRM system to access customer data and history.
- External data sources: Leverage external data sources for market insights, competitor analysis, and trend forecasting.
- Fact-checking: Implement mechanisms to verify information against trusted sources and flag potential inaccuracies or inconsistencies.
- Continuous learning: Design systems for the AI agent to continuously learn and update its knowledge base with new insights and data.
Incorporate reasoning and analysis capabilities
- Data analysis: Implement algorithms for data analysis, including statistical analysis, pattern recognition, and trend identification. This can be used for market research, customer segmentation, and sales forecasting.
- Sentiment analysis: Analyze customer feedback to understand sentiment towards products, brands, and customer service.
- Recommendation systems: Develop systems that leverage customer data and product information to provide personalized product recommendations.
Design output generation and interaction
Natural Language Generation (NLG) allows developing capabilities to generate human-like responses and product descriptions.
- Query refinement: Implement features that allow customers to refine their queries and receive more precise results.
- Personalization: Implement techniques to tailor responses based on customer profiles and preferences.
- Multilingual support: Create modules for translating and localizing content for global markets.
- Feedback mechanism: Provide a mechanism for customers to provide feedback on the AI agent’s performance and suggestions.
- Visualization: Create modules that can generate charts, tables, and other visualizations to present data in an easily understandable format.
Implement ethical and bias mitigation measures: Fairness in recommendations
Ensure product recommendations are not biased towards certain brands or demographics.
- Bias detection: Develop systems to detect and mitigate potential biases in data, algorithms, and outcomes.
- Transparency: Implement measures to explain product recommendations and pricing decisions.
- Data protection: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR.
Create user interface and interaction design: Making the agent user-friendly
- Intuitive interface: Create an easy-to-use interface that allows customers to interact with the AI agent naturally. This could include chatbot interfaces, voice assistants, or personalized recommendations within the website or app.
- Omnichannel support: Develop interfaces for various channels (e.g., website chatbot, mobile app, voice assistants).
- Visual search: Implement image recognition for product searches.
- Query refinement: Implement features for query refinement, allowing users to iteratively refine their search queries and receive more precise results.
Testing and validation: Ensuring accuracy and reliability
- Rigorous testing: Conduct thorough testing of the AI agent’s capabilities across various retail tasks and scenarios.
- Validation studies: Compare the AI agent’s outputs to human expert analysis to validate its accuracy and reliability.
- Ongoing monitoring: Implement ongoing monitoring and quality control measures to ensure the agent’s performance remains consistent over time.
Deployment and scaling: Making the agent accessible
- Infrastructure: Set up the necessary infrastructure to deploy the AI agent, considering factors like computational resources, storage capacity, and security.
- Data security: Implement robust security measures to protect customer’s confidential data.
- Scalability: Develop strategies to scale the AI agent’s capabilities to accommodate increased transaction volumes and users.
- Mobile optimization: Optimize the AI agent for mobile commerce.
- Integration: Ensure seamless integration with existing e-commerce platforms and CRM systems.
Continuous improvement and updating: An ongoing journey
- Feedback loops: Establish feedback loops to gather user input and continuously improve the AI agent’s performance.
- Regular updates: Regularly update the agent’s knowledge base with the latest research findings and data. This includes new fashion trends, product launches, and market shifts as well as seasonal adjustments.
- Performance analytics: Implement systems to track KPIs such as conversion rates, average order values, and customer satisfaction scores.
- Version control: Implement version control and change management processes to track updates and ensure stability.
Documentation and training
- Staff training: Develop programs for retail staff to work alongside AI agents.
- Customer education: Create guides to help customers effectively interact with AI assistants.
- Best practices: Establish guidelines for AI-assisted customer service and sales.
Platforms for building AI agents
- AutoGen (from Microsoft): A framework specifically designed for building conversational AI agents using LLMs. It simplifies creating agents to engage in multi-turn conversations, access tools, and perform complex tasks.
- Crewai: A no-code platform for building and deploying AI agents, including those powered by LLMs. It offers a user-friendly interface for defining agent workflows, integrating data sources, and managing agent interactions.
Key considerations
- Human-AI collaboration: Remember that AI agents are tools designed to augment human intelligence, not replace it. Foster a collaborative environment where AI agents and teams work together to achieve common goals.
- Customer privacy: Prioritize the protection of customer data and obtain necessary consent for AI interactions.
- Ethical implications: Be mindful of the ethical implications of AI in retail and e-commerce, ensuring that your AI agent is developed and used responsibly, transparently, and in a way that benefits society as a whole.
Building LLM-powered AI agents for retail and e-commerce is an iterative journey of continuous learning and improvement. By following this guide, you can create a powerful e-commerce assistant that enhances customer experiences, optimizes operations, and drives growth in the competitive retail landscape.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
How can LeewayHertz help you build AI agents for retail and e-commerce?
LeewayHertz is uniquely positioned to empower retail and e-commerce businesses to harness the power of AI agents. With our extensive expertise in AI solutions tailored for the retail and e-commerce sector, we can help you enhance customer engagement and streamline your operations by integrating advanced AI agents into your technology ecosystems. Here’s how LeewayHertz can assist your retail-focused enterprise in leveraging AI agents effectively:
Strategic consultation: LeewayHertz offers strategic consultation to help retailers understand the potential of AI agents. Our experts assist you in identifying key areas within your retail operations where AI agent can provide significant benefits. We develop customized strategies for digital transformation that align with your business goals, focusing on enhancing customer experiences, optimizing inventory management, and improving marketing effectiveness.
Custom AI agent development: We specialize in developing custom AI agents tailored to the unique needs of the retail sector. Utilizing advanced frameworks like AutoGen Studio for rapid prototyping and CrewAI for orchestrating collaborative AI functionalities, we ensure that the AI agents developed are perfectly suited to handle specific retail tasks, whether they’re related to personalized shopping experiences, customer service, or supply chain management.
Training and data management: LeewayHertz handles the collection, cleaning, and organization of data required to train AI agents. They also manage the ongoing process of training models with new data to improve accuracy and adapt to changing business needs, ensuring AI agents remain effective and relevant.
Seamless integration: Our team expertly integrates AI agents into your existing retail systems. We ensure that these intelligent systems work in harmony with your current IT infrastructure, enhancing data interoperability and operational efficiency without disrupting ongoing processes. This integration is crucial for maintaining a unified customer experience across all digital and physical touchpoints.
Continuous support and optimization: LeewayHertz’s commitment to its clients extends beyond the initial deployment of AI agents. We provide continuous support, monitoring, and optimization services to ensure that your AI solutions adapt to evolving market conditions and consumer behaviors. Our ongoing support helps keep your AI agents at the cutting edge of technology, ensuring they continue to drive value for your business.
Driving innovation in retail: In an industry where customer engagement and operational efficiency are key, AI agents developed by LeewayHertz offer retail businesses a competitive edge. Our AI solutions are designed to enhance the shopping experience, improve the accuracy of inventory forecasts, reduce operational costs, and provide personalized customer interactions that meet the high expectations of today’s consumers.
In conclusion, partnering with LeewayHertz gives retail and e-commerce businesses access to the expertise and technology necessary to develop and integrate AI agents that will drive business growth and innovation. As AI continues to transform the retail industry, LeewayHertz is dedicated to ensuring that its clients are well-equipped to leverage these advanced technologies, securing their position at the forefront of the retail sector.
Looking ahead: Future directions for AI agents in retail and e-commerce
This section highlights the major future trends of AI agents across retail and e-commerce.
Enhanced cognitive capabilities
Future LLM agents are expected to exhibit advanced reasoning and cognitive capabilities, enabling them to handle complex customer queries and provide solutions considering long-term customer value. These agents can perform multi-step tasks and make decisions that reflect a deeper understanding of the retail environment.
Seamless multimodal interactions
As LLM agents evolve, they will manage seamless interactions across multiple modes of communication, including text, voice, and visual inputs, providing a cohesive and integrated customer experience regardless of how shoppers interact with the brand.
Greater personalization at the scale
It’s well-known that greater personalization makes for happier shoppers. In fact, 70% of customers spend more with brands that offer more personalized customer experiences. LLM agents will drive unprecedented levels of personalization, using detailed insights gathered from customer data to tailor the shopping experience in real-time. This includes personalized marketing, dynamic pricing, and customized product recommendations that adapt to customer preferences and behaviors as they shop.
Ethical AI and improved trustworthiness
As these technologies become more prevalent, there will be an increased focus on ethical AI practices. LLM agents will be developed with a strong emphasis on fairness, transparency, and privacy, ensuring they earn and maintain customers’ trust and comply with regulatory standards.
Integration with IoT and smart devices
Integrating LLM agents with IoT and smart devices will enable more dynamic interactions in the physical retail space. For example, smart shelves equipped with AI could provide personalized messages and offers to customers as they browse in-store, enhancing the omnichannel experience.
Voice commerce expansion
With voice assistants projected to double in presence by 2024, reaching over 8.4 billion units globally, voice commerce is anticipated to grow exponentially. AI-powered voice assistants will facilitate easier shopping, enabling voice-activated purchases, order tracking, and customer inquiries, making shopping as simple as giving a command.
Visual search enhancement
AI-powered visual search capabilities are set to transform how consumers find products. Shoppers can upload images or use their smartphone cameras to discover products instantly. This technology reduces the friction in the product discovery process, catering to the visual preferences of modern consumers.
AI-driven sustainability
Sustainability is an increasingly important concern for both consumers and businesses, with 78% of consumers prioritizing sustainability, and 84% of saying that poor environmental practices would alienate them from a brand or a company. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, AI agents will play a pivotal role in helping retailers reduce waste through better inventory management and demand forecasting. They will also help promote sustainable products to consumers who prefer eco-friendly options.
Robust fraud detection and security
Enhanced security protocols powered by AI will become critical as e-commerce transactions continue to grow. LLM agents will offer robust fraud detection capabilities by analyzing patterns and spotting anomalies in real time, thereby protecting both the retailer and the consumer from potential threats.
The future of LLM agents in retail and e-commerce represents a blend of technological advancement and customer-centric innovation. Retailers who adopt these advanced AI capabilities will be well-positioned to meet their customers’ evolving expectations, offering experiences that are not only seamless and personalized but also engaging and secure.
Endnote
As we look towards the future of retail and e-commerce, the role of AI agents is becoming increasingly central, driving us towards a new era of innovation and customer engagement. The insights provided in this article demonstrate the profound impact AI agents are expected to have on the industry, streamlining operations, enhancing customer experiences, and introducing transformative service capabilities.
Retailers who adopt AI agent technology are positioning themselves at the cutting edge of a market that values efficiency, personalization, and seamless consumer interactions. These technologies optimize day-to-day operations and open up new opportunities for connecting with customers in meaningful and engaging ways.
However, the advancement of AI agents comes with a responsibility to implement these technologies ethically and transparently, especially concerning consumer privacy and data protection. Success in the evolving retail landscape will depend not only on how retailers leverage AI technology but also on how they uphold and prioritize the trust and security of their customers.
Moving forward, businesses in the retail and e-commerce sectors must continue to adapt and innovate, ensuring that AI agents are used not just for economic gains but also to enhance the overall shopping experience. By doing so, they can deliver on the promise of AI to provide value that resonates well with the expectations of modern consumers.
As we continue to explore and integrate these sophisticated AI solutions, it’s clear that the journey ahead will be marked by continuous learning and adaptation. For retailers ready to embrace this change, the future is bright, with possibilities to redefine the marketplace and achieve new levels of success. Let’s embrace these changes with a strategic focus and a commitment to excellence, ensuring that as the retail world evolves, it does so in a way that is beneficial for both businesses and their customers.
Ready to transform your retail business with AI agents? Explore LeewayHertz’s AI agent development services to streamline operations, personalize customer interactions, and drive growth today!
Start a conversation by filling the form
All information will be kept confidential.















